As a ‘yellow alert’ has been issued, yet again, in Bengaluru, citizens search for answers on the reasons for the severe floods this year. One such explainer is by Arun Pai, founder of Bangalore Walks.
In a series of videos, titled ‘Floodsplaining’ posted on the Bangalore Walks YouTube channel, Arun Pai deep dives into questions on the causes of the floods. He does not pass any value judgements and focuses on the scientific reasons for the severe floods.
His videos are based on his extensive research, including talking to experts, reading on the topic, and gaining insights by going around the Bengaluru tank network and the Mahadevpura plains on bike and by foot. He says that he is not an expert, but is on a quest to understand the various aspects of the situation out of curiosity and his love for Bengaluru.
Why gradient matters
Citizen Matters, in earlier articles, has summarised and republished the first three episodes of Arun Pai’s videos. In the fourth episode, titled ‘Gradient Matters. How steep is your slide?’ Arun Pai, with the aid of a topographical map, trivia, historical events, and a dash of humour, highlights why gradient is important to understand why the city floods after heavy rains.
Read more: How open data, wastewater reuse and other measures can prevent flooding in Bengaluru
Bengaluru’s topography
Unlike Chennai, Delhi, Mumbai, and Kolkata, Bengaluru is not a flat city. It has an undulating topography and gradients vary considerably across the city. Gradient is important because it affects the speed at which water travels downstream.
Arun Pai recommends an app to viewers called topographic-map.com (one can also do a Google search of ‘Bengaluru topographic map’ to find the app. He demonstrates how the alitude above sea level is displayed when you click on anywhere in the map.
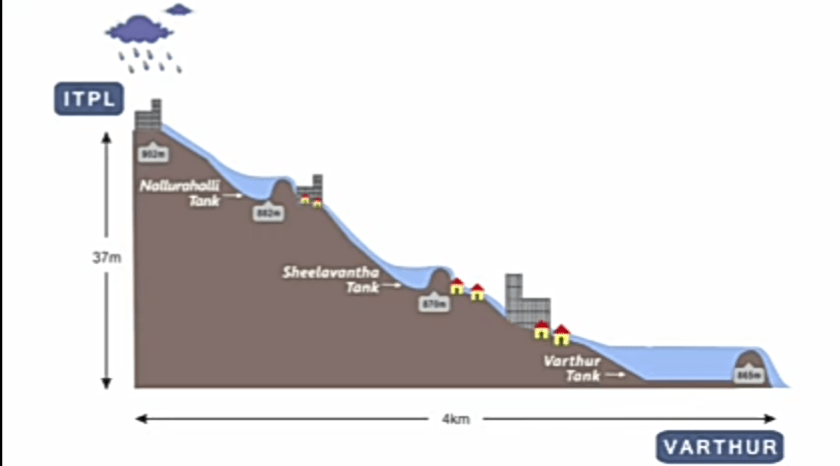
Arun Pai uses maps and graphs to explain why Bengaluru floods. Pic courtesy: Bangalore Walks YouTube channel
The flow of rain water
The meme of how Bengaluru transformed into a giant waterpark after heavy rains, is turned on its head by Arun Pai. He does so by urging the viewers to imagine, as an analogy, the city as a giant waterpark with several high points and how all the water slides eventually end up in a large pool of water. He then looks at how rain water flows from different points: ITPL, Tin Factory, Silk Board, and Domlur, into Varthur tank.
Read more: Rainbow Drive — layout or lake? The man-made tragedy of Bengaluru’s flood-prone neighbourhoods
A feat of human engineering
Tanks were built to capture rain water so that it could be utilised for irrigation purposes. Arun Pai adds that Bengaluru history includes a feat of human engineering. It is part of one of the oldest and most sophisticated rain water harvesting systems in the world, a fact that must not be lost in time and must be remembered and understood, especially in the current times.
Watch the full video here:
Episode 4 of Floodsplaining series. Video: Bangalore Walks
[The video has been republished with permission]