Citizens, activists and lake groups are taking up the cause of protecting and improving Bengaluru’s lakes. Engaged citizens and government agencies need to work together to restore to Bengaluru its old reputation of being the “city of lakes’. But there is widespread confusion on whom to approach regarding specific issues. The chart below shows the various government bodies involved with lakes and the current governance structure.
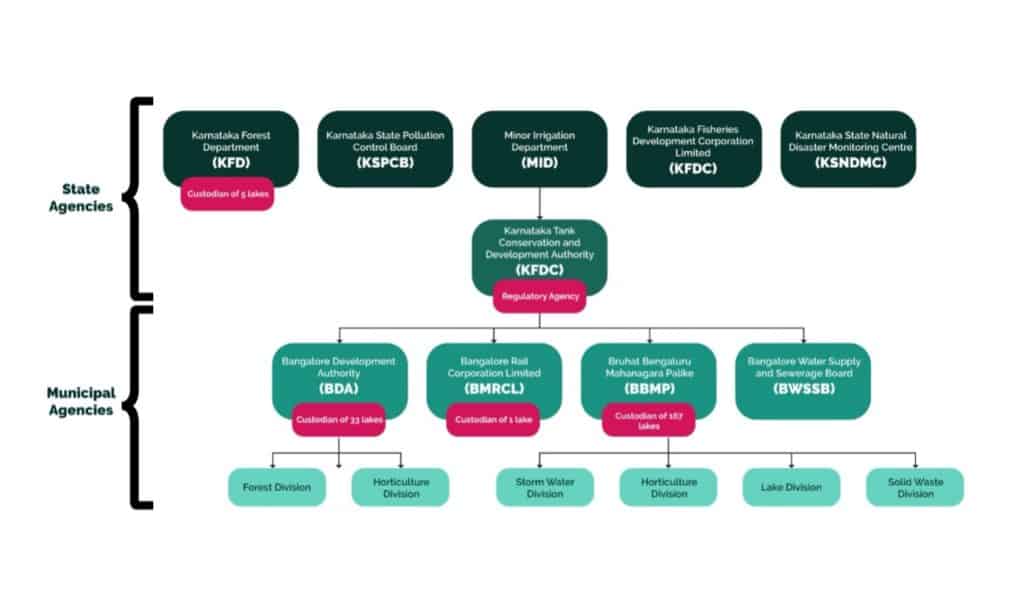
A list of government bodies responsible for the physical, chemical and ecological status of respective lakes are given here.
Read more: MOUs or no MOUs, citizen groups continue the fight to save Bengaluru’s lakes
In 2018, the Government of Karnataka (GoK) repealed the Karnataka Lake Conservation and Development Authority (KLCDA) Act and transferred all the responsibilities of the department to Karnataka Tank Conservation and Development Authority (KTCDA), which falls under the Minor Irrigation Department (MID) and is chaired by the Chief Minister. KTCDA is the regulatory agency for all lakes in the state but the custody of lakes is still under local government agencies. In Bengaluru, lakes come under BBMP, BDA, KFD, and BMRCL.
For most issues pertaining to a lake, you can contact the lake custodian but if the lake custodian is not responding you can contact MID at 080-2663 2102.
Most of these lakes have lake groups formed by residents and ecologists who are keen to improve the ecological status of lakes. A list of lakes and the lake groups and contact information of the person spearheading the group can be found here.
Read more: Surveying maps, roping in authorities and building a community for Bengaluru’s lakes
Departments and when you should approach them






Good Morning, I would like to bring to your notice a lake in Kadugodi near Sharada Vidya Mandir,which is in a dilapidated condition and needs to be restored.
Respected Sir/Madam, I sincerely request your kind attention towards the cleaning and proper maintenance of LAKSHMIPURA LAKE in LAKSHMIPURA VILLAGE of MADANAYAKANAHALLI,TUMKUR ROAD
. At present, it is facing pollution and neglect, which could have long-term effects on public health and groundwater. I kindly urge the authorities to take timely action for desilting, cleaning, and preventing sewage/waste dumping, and also to consider sustainable measures