If you were to ask any commuter in any Indian city about their daily pet peeve, it would be the time spent in traffic.
And now, Ola, the new age mobility platform serving 110 cities with 8 lakh vehicles on the roads has presented a year-end glimpse of ‘how India commuted’ based on their records.
Some highlights from the top seven cities – Mumbai, Bangalore, Delhi, Hyderabad, Pune, Kolkata, and Chennai:
- Total average traffic speed dropped by a whopping 2.9km/hr with Bangalore registering the slowest at 17.2km/hour
- Ola Share has saved 4 times the fuel from last year, telling of the high customer adoption rate
- Delhi tops as the city that shares the most
- 666 years worth of time has been spent in engaging with Ola Play, consuming 480 TB of data every month
- Ola Outstation has covered India’s road length 53 times, covering 17.35 cr kms across 800 destinations
Here’s a more detailed look at the mobility patterns in our cities, in five interesting infographs:
[All information and graphics here have been taken from a Press Note issued by Ola, and published here with minimal edits]
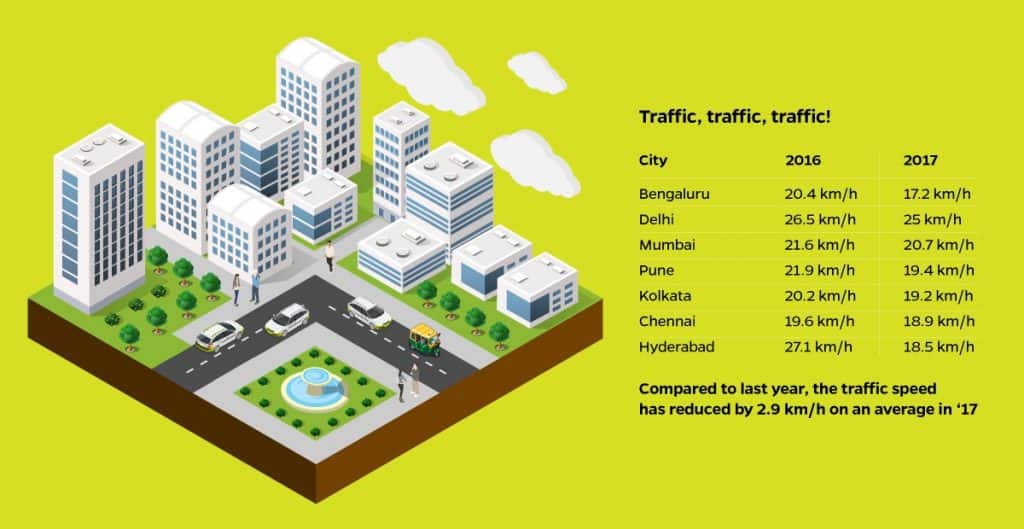

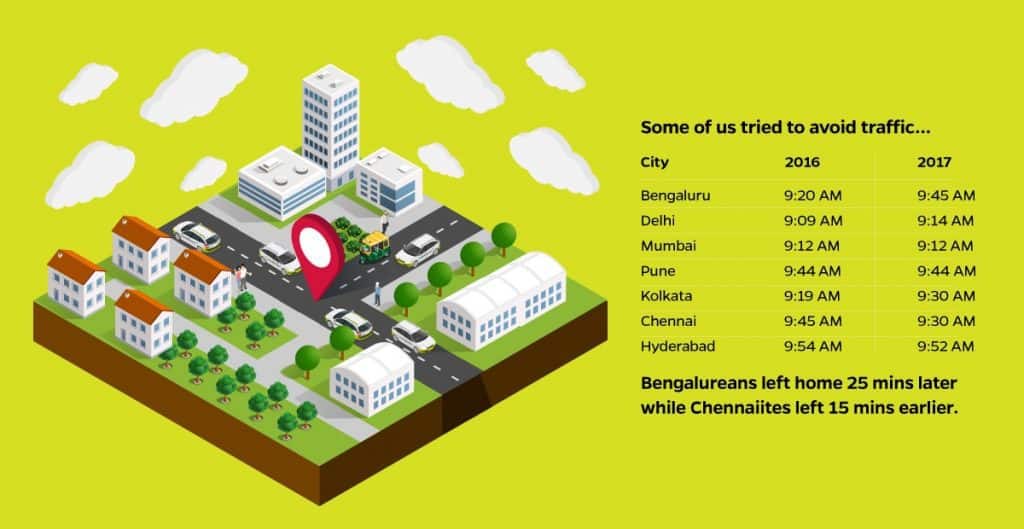
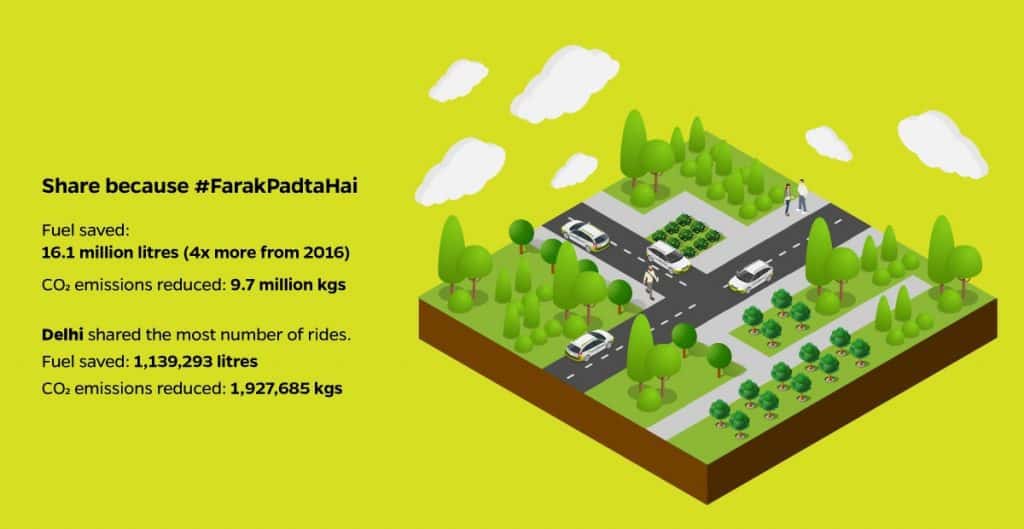
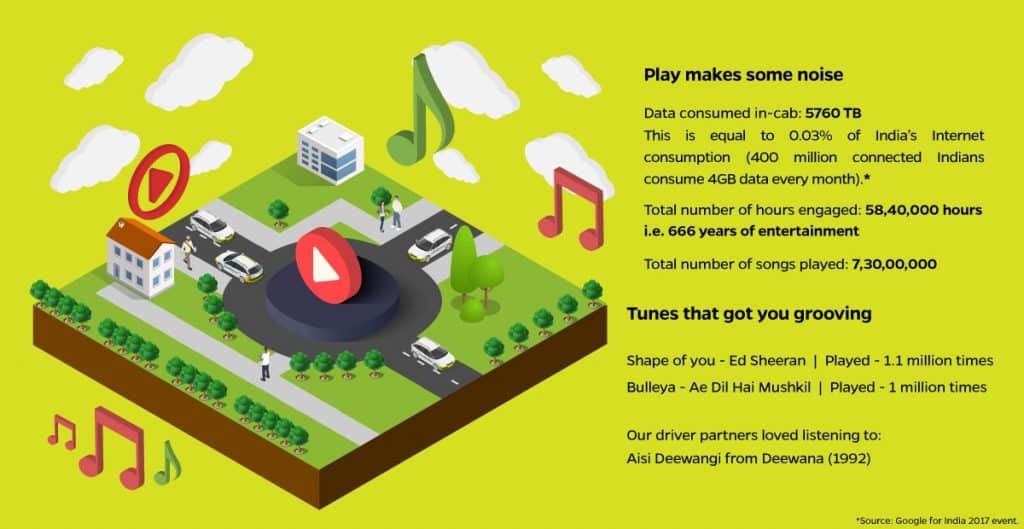
Despite Namma Metro’s Phase One becoming operational, Bangalore’s traffic speeds have slowed down. Outlines the necessity for faster construction of phase two of Metro and introduction of suburban rail.
Lazy Governments could not care less!