Solving their civic-woes has been a challenge for the 12 lakh residents living in the 110 villages on the outer circle in the Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP) limits, in Bengaluru. Not only has the struggle to get drinking-water been unfruitful, the lack of drainage network lets the sewage accumulate in open drains and lakes, causing irreversible long-term ecological and health problems.
There is, however, about to be a slight change in their plight. The infrastructural work to lay underground drainage facilities in the five zones — Mahadevapura, Byatarayanapura, Bommanahalli, Dasarahalli and RR Nagar — officially commenced on March 15, 2018 and March 19, 2018 respectively. A progress-review report presented during a meeting at the Bangalore Water Supply and Sewerage Board (BWSSB) head office on May 26, 2018 says that 36 months is the timeline set to complete building the sewerage system for the 225 sq km added to BBMP in 2007. That means by March 2021, the sewage network will be connected to the erstwhile villages.
Most importantly, a presentation by BWSSB in possession with Citizen Matters reveals that 14 STPs and 7 Intermediate Sewerage Pumping Stations (ISPS) have been proposed by the board (table below).
The table below shows the locations and capacities:
Proposed STPs and ISPS under the Cauvery Water Supply Stage V scheme Source: BWSSB
| Zone | STPS | MLD | ISPS | MLD |
| Bytrayanapura | Jakkur | 7.0/11.0 | Bellahalli | 0.9/1.5 |
| Yelahankakere | 6.0/15.0 | |||
| Doddabettahalli | 7.0/11.0 | |||
| Bilishivalli | 17.0/27.0 | |||
| Mahadevapura | Varthur | 15.0/24.0 | Hagadur | 15.0/24.0 |
| Bommanahalli | Pilaganahalli | 4.06/6.0 | Naganathapura | 9.0/13.0 |
| Thalaghattapura | 5.0/8.0 | |||
| RR Nagar | Somapura | 8.0/12.0 | Arehalli | 1.1/1.7 |
| Hemmigepura | 13.0/20.0 | Hemmigepura | 1.7/2.5 | |
| Dasarahalli | Kariobavanahalli | 10.0/16 | Herohalli | 0.5/0.7 |
| Herohalli | 3.0/5.0 | Doddabidarakullu | 8.1/ 2.8 | |
| Hosahalli | 6.0/10.0 | |||
| Chikkabanavara-2 | 4.0/10.0 | |||
| Nagasandra | 9.0/13.0 |
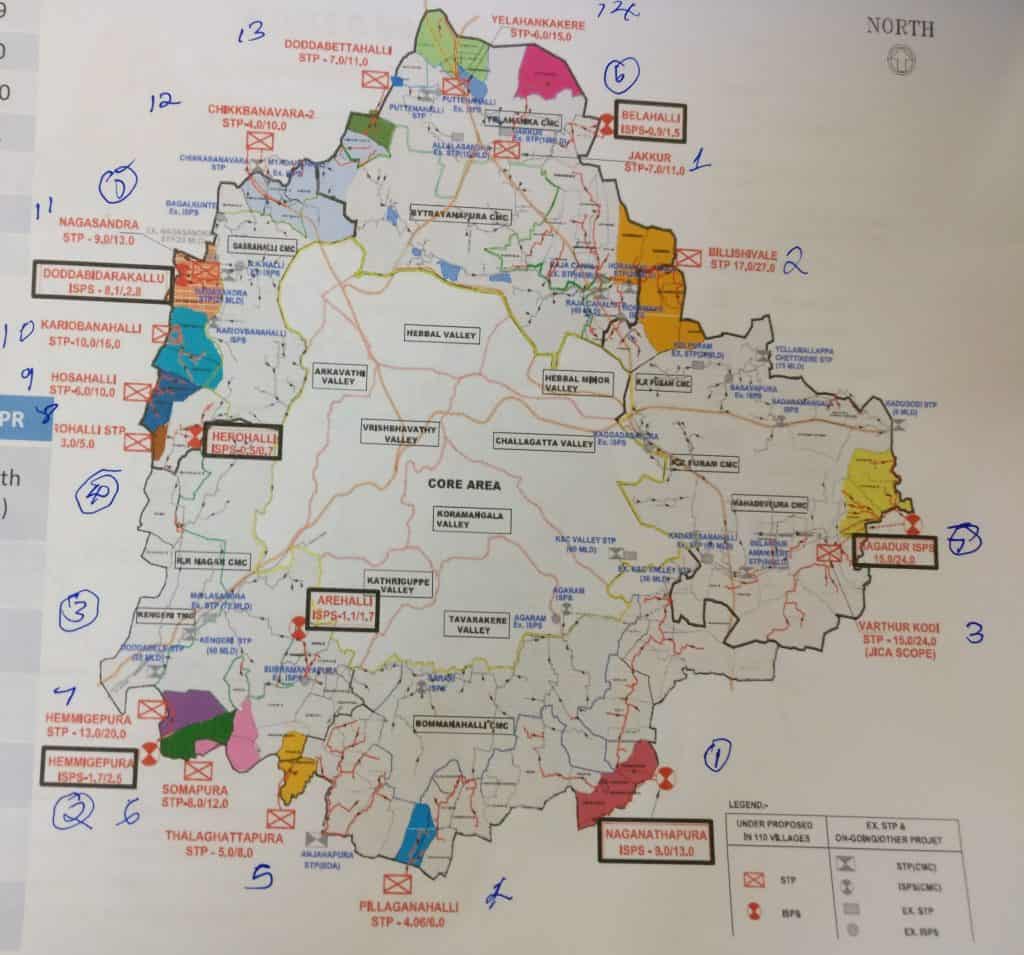
The map of proposed STPs. Source: BWSSB/JICA
There are two Detailed Project Reports that were prepared to avail the loan from JICA. The approved DPR does not contain the plans for sewers and house constructions. Instead, it sticks to the projected increase in sewage generation up to 2049 and the proposed Sewage Treatment Plants. The reason is that the first DPR prepared in September 2016 already had a networking plan of lateral sewers and was hence excluded, which the department plans to use for reference.
Projected sewerage generation
The villages became a part of Bengaluru when Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BMP) became Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP) by expanding to accommodate 7 city municipal councils, 1 town municipal council and the 110 villages. This was largely unplanned, and increased the burden of sewerage. Sewage from Bengaluru area is projected to reach 1345 MLD by 2019 – almost equivalent to the city’s daily water-distribution (1400 MLD).
JICA claims that the existing 14 Sewerage Treatment Plants (STPs) within BBMP area had the capacity to treat 57.4% of sewerage in 2016. The JICA Preparatory Survey makes an ambitious estimation of capacity to process a good 97% of the waste water by 2034. The below table shows the projected growth of sewage generated in the city’s core areas, ULBs and 110 villages up to 2049.
| Area | 2016 | 2019 | 2024 | 2034 | 2049 |
| Core | 745 | 762 | 792 | 856 | 961 |
| ULBs | 323 | 366 | 447 | 634 | 1,005 |
| 110 Villages | 190 | 217 | 263 | 372 | 587 |
| Total | 1,258 | 1,345 | 1,502 | 1,862 | 2,553 |
Source: JICA Preparatory Survey. (MLD)
Budget for sewage lines
The work to provide sewerage facilities is being taken up in three packages.
- The first package (Byatarayanapura and Mahadevapura) is estimated at Rs. 327.11 crore.
- Bommanahalli will be taken up in the second package costing Rs. 301.55 crore.
- Dasarahalli and RR Nagar in the third package will cost Rs 296.38 crore.
The BWSSB in its progress report has mentioned the period of completion as 36 months. It implies that by March 2021, all the 110 villages would have a fully functional drainage system.
The Bangalore Development Authority (BDA) is managing the upkeep of the villages, which also have layouts for bank employees and revenue officials. It still took a decade to get administrative approval to start drainage work, which came as late as 2017 under the order number UDD-174 MNI 2017, issued on November 7, 2017. The order gave the BWSSB the permission to start establishing the entire sewerage network at a cost of Rs 1,000 crore combined with STPs and ISPS projects.
Unlike the water distribution-network which is being funded by the Japanese agency JICA, the Karnataka government is pooling in half the amount by bearing Rs 500 crore for the sewerage network. The first half ( Rs 250 crore) is being given through a grant and the other Rs 250 crore is being loaned to BWSSB.
The below table offers a breakdown of the finances and timelines.
| Zone | Contractor | Awarded cost | Commencement Date | Period of completion | Date of completion |
| Byatarayanapura
& Mahadevpura |
M/S Khilari Infrastructure Pvt Ltd | Rs 327.11 crore | 15.03.2018 | 36 months | 14.03.2021 |
| Bommanahalli | M/S Larsen & Toubro Ltd | Rs 301.55 crore | 19.03.2018 | 36 months | 18.03.2021 |
| R R Nagar & Dasarahalli | M/S Larsen & Toubro Ltd | Rs 296.38 crore | 19.03.2018 | 36 months | 18.03.2021 |
| Total: 925.04 |
Source: BWSSB
The GoK and BWSSB are sharing the cost by dividing Rs 500 crore each. Bangalore Water Supply and Sewerage System (BWSSB) is also using their own funds of Rs 500 crore through the finance collected from Beneficiary Capital Contribution (BCC), Greater Bangalore Water And Sanitation Project (GBWASP) and AMRUT (Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation) scheme.
This concept was followed in constructing sewage networks in the eight Urban Local Bodies added in 2007, for which funding was generated through the same channels.
Also read: Part I of this series covering the status of water network for 110 villages.
Dear citizen matters. I am constructing a small house in byrathi, however there is no sewage connection there in the layout called Athmavidya nagar. All grey water is let in the drainage causing foul smell and breeding ground for mosquitoes. The above article mentions Mahadevapura areas was taken by M/S Khikari pvt lts company. I believe Byrathi area falls under this constituency. There has been no sewage lines even as 300plus houses are in this layout. Cauvery connection has just started. when will we see sewage lines being laid?
many thanks.