Chennai saw record downpour over the weekend, with many parts receiving levels of rainfall not seen since 2015. Many parts of the city have been inundated after the heavy spell that followed the onset of the northeast monsoon. Water-logging has made roads dangerous and unnavigable in many parts of the city. Water entered homes and other buildings and residents in low-lying areas has to be evacuated on emergency as a result of the urban floods.
As in many other Indian cities, in Chennai too, a wide range of issues are responsible for urban flooding. The host of problems at the root of flooding have only been getting worse in recent years. If these issues are left unaddressed, Chennai is unlikely to solve any of its flooding-related problems in the coming 10 years.
Expansion leading to urban floods
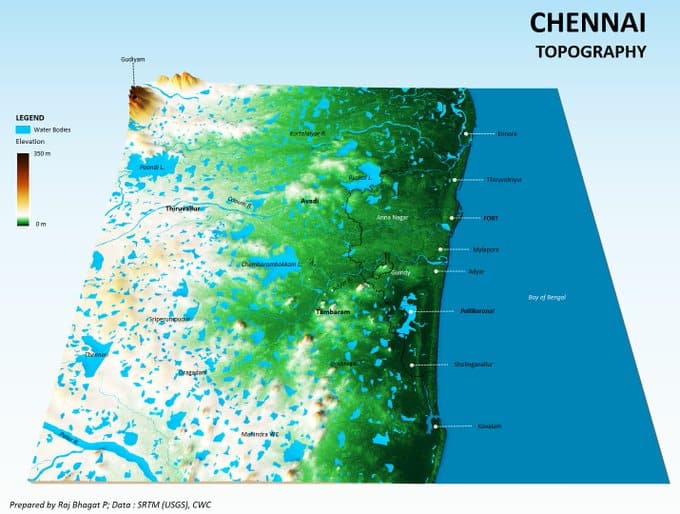
Chennai Metropolitan region, in particular the area under the Chennai Corporation, is relatively flat terrain that is very close to sea level. In the past, the agricultural activity in the region had prompted construction of thousands of lakes, shallow and large.
Over the years, the expansion of the city saw buildings come up in low lying areas and wetlands, which are extremely close to sea level. In such instances, water would tend to stagnate, as experienced during the historic floods of 2015.
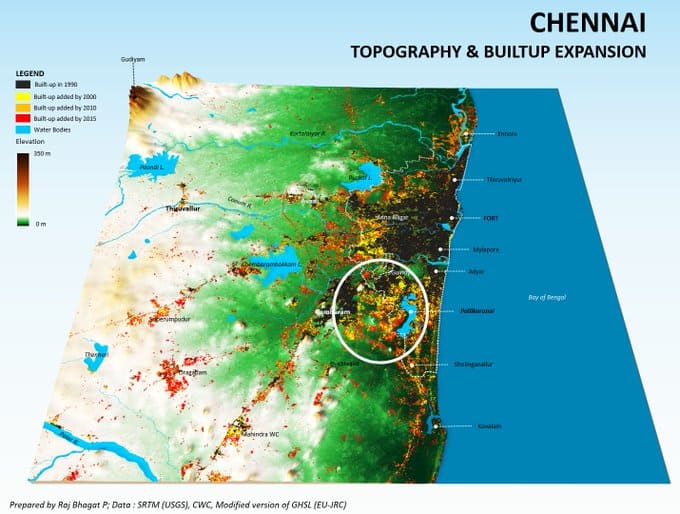
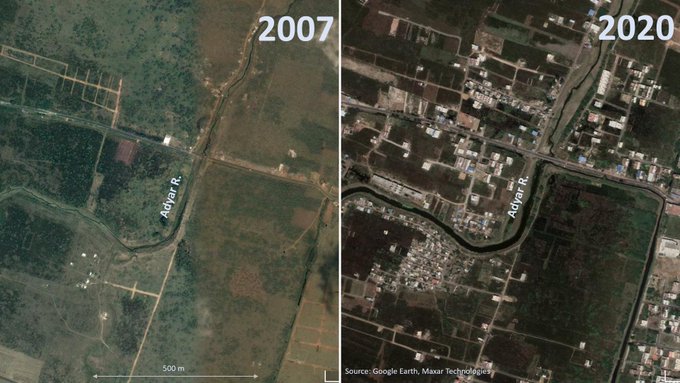
Despite recent instances of multiple floods, the floodplains of rivers like the Adyar are rapidly getting converted into urban areas for residential, commercial and industrial purposes. With many of these structures already complete, it would be impossible to bring these sites back to their original state.
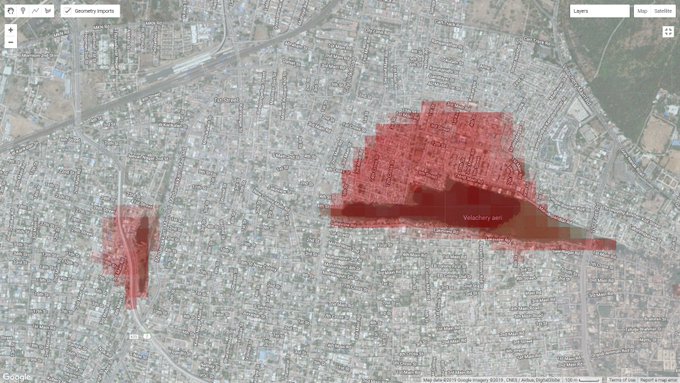
As an example, some of the areas near Adyar river that were flooded during 2020 are shown in the map below, which is based on satellite data.
Some natural water bodies and wetlands such as Pallikaranai, which could act as buffer in case of heavy downpour, are also being converted into built up areas leaving the water nowhere to go. Already existing built up areas have also fast densified over the years, which means there is significantly less penetration of water into the ground, leading to situations like we see at present.
Read more: Madipakkam: Where roads disappear after a few spells of rain
Artificial infrastructure fails to stop urban floods
Since there is no green infrastructure to help the city in such instances, one would expect artificial infrastructure to step up. However the street design, storm water drain design and construction of the same fall woefully short in coming to the city’s rescue at times such as this.
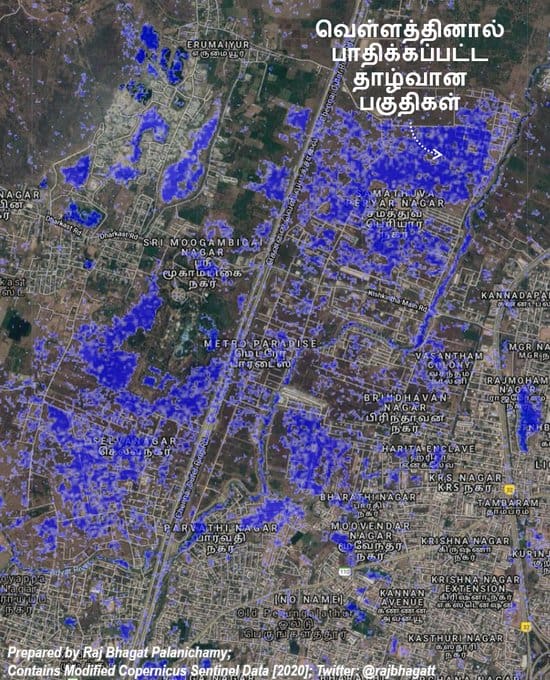
The artificial lakes which once served the agricultural lands could have been repurposed and engineered to act as buffers. However, they have either been lost to time or are at reduced capacity due to sewage discharge. Some of them are not engineered to act as buffers. The map below shows the loss of Velachery Lake over time.
Read more: Rivers remember, but why don’t we?
Lack of scientific planning
Neither the city’s Master Plan nor the city’s Disaster Management Plan addresses the issue of flooding in a scientific manner. The Disaster Management Plan (2017) has some SOPs; however, they offer no scientific explanation, location-specific detailed action plans or a roadmap to solve this issue.
Even with proper planning, revamping street design and scientific storm water drain design and their execution could cost crores and many more years to function effectively.
Gaps in governance
Urban floods are not just a result of improper flood management. It is also a result of gaps in governance. With unelected officials who lack any kind of accountability to the local public, it is impossible to get people’s concerns addressed. For the past six years, the city has had no elected local body due to the delay in conducting local body polls.
Along with scientific rigour in designing for such events, municipal governance reforms are also necessary. Even with such measures, the planning and execution of steps to make Chennai flood proof may be many years in the making.
Even so, we must press for a long-term road map to be drafted for the city so that in ten years, the city could be relatively safe and liveable despite the rains.
[This article is based on a series of tweets made by the author through his personal Twitter handle.]

Due Respects to Dr Raj Bhagat:
When we have areas with names on suffix as “eri”, “karanai” , caution exists its water, we are dealing with.
GCC Has no Authority in going for Development of complexes at such areas.
Chennai has a water body by way of B
“Buckingham Canal” existing at City from North to South say 40km parallel to EC, this can serve as a relief canal ie when N floods can release to S and vice versa. It has controllable outlets to Sea along coast. City Planners could explore how to use them. Mr Narasiah Sir had once suggested to put this to right use.
Our Daily newspapers need to give caution to Chennai Readers on timings of HighTide and LowTide happening daily. Possibility of our Lake flood gates kept open at HighTide timings can not be ruled out..
O&M practices of all lakes and ponds by way of desilting them, And where needed additional depths added in the W/bodies..
Will like to expand some of the points, if need arises..
Notings Issued in doing social and Environmental good to communities .
Well wishes.