For the past three years, Seema, a 35-year-old healthy woman has been running all outdoor errands for her family. She lives with her six-year-old son, her 42-year-old wheelchair-ridden husband, and a 70-year-old mother-in-law in a humble middle-income household. After her husband met with a road accident and lost his ability to walk, the family has been increasingly cautious about their outdoor activities.
Seema’s aged mother-in-law and disabled husband almost never leave the house unless a special van is rented. Seema always walks her son to and from the school bus, and at no time is he allowed to walk by himself. Her primary mode of transport is walking, taking the Metro, or hiring a cab/van. The couple has avoided having a second child because a pregnant Seema’s movement would then be limited, and the family would be rendered helpless.
Like Seema and her family, many Bengalureans face great obstacles to simply walk safely in their neighbourhoods. Pedestrians are forced to share space with vehicles on the road, for reasons ranging from broken footpaths to the complete absence of one.
Bengaluru has a total road network of 14,000 km. But footpaths are present along only around 47% of the network, and even their utility is limited due to widths below the standard of 1.5-1.8 m prescribed in IRC (Indian Road Congress) guidelines, encroachment by street vendors, illegal parking, unevenness, damage, etc.
Little action from authorities despite pedestrian deaths
Earlier this year, the Karnataka State Legal Services Authority (KSLSA), on the directions of the High Court, solicited inputs from citizens on the status of the city’s roads and footpaths. Of the 5,435 responses KSLSA received, the majority (4,998) were related to footpaths. Of these, 3,531 responses were about blocked footpaths (garbage, street vendors and parked vehicles), 1,443 about damaged footpaths, and 24 about the absence of footpaths.
Such insufficient road infrastructure causes high death rates among road users, especially pedestrians. Bengaluru recorded 276 pedestrian deaths in 2018, and 272 in 2019. Bengaluru Traffic Police (BTP) data indicates that, between 2017 and 2020, pedestrians made up 37% of the deaths from road crashes.
Read more: The pedestrian is a nobody: Bengaluru’s footpath story
According to NCRB (National Crime Records Bureau) data, 25,858 pedestrians were killed in road accidents nationwide in 2019. Their numbers came to 17% of the 1.5 lakh road accident victims that year.
Some groups more at risk
Healthy pedestrians manage to navigate roads without losing limb or life, but more vulnerable users like children, older adults, individuals with disabilities, labourers carrying heavy loads, and women – especially pregnant women – face significantly higher amounts of risk, and are more exposed to road crashes and injuries. Data from BTP and NCRB indicates that, in Bengaluru, a third of pedestrian deaths is that of senior citizens.
At the national level, NCRB data indicates that road crashes are the leading cause of accidental deaths among children aged 0-18 years (50%), and the second most common cause among older adults aged 60 and above (23%).

Studies in Bengaluru show that of all children killed in traffic incidents, 51% are pedestrians. As per the estimates of WRI (World Resources Institute) India, about 90% of children in Bengaluru live within 5 km from the school they attend, and 58% of them walk to school. Given that crash risks are higher in children during school commute, the Safe Access to Schools (SATS) tool was jointly developed by WRI India and Underwriters Laboratory (UL) recently, to help identify pedestrian crashes and fatalities in school walking zones.
Insights from this tool indicate that, in 2019, 227 (31%) of pedestrian crash fatalities and 46 (6%) of child fatalities in the city happened within 250m of a school walking zone. Fifty per cent of the pedestrian deaths occurred on major arterial roads, and 20% near Metro and bus stations.
Read more: Why addressing pedestrian concerns is key to making Bengaluru liveable
What makes Bengaluru pedestrian-unfriendly?
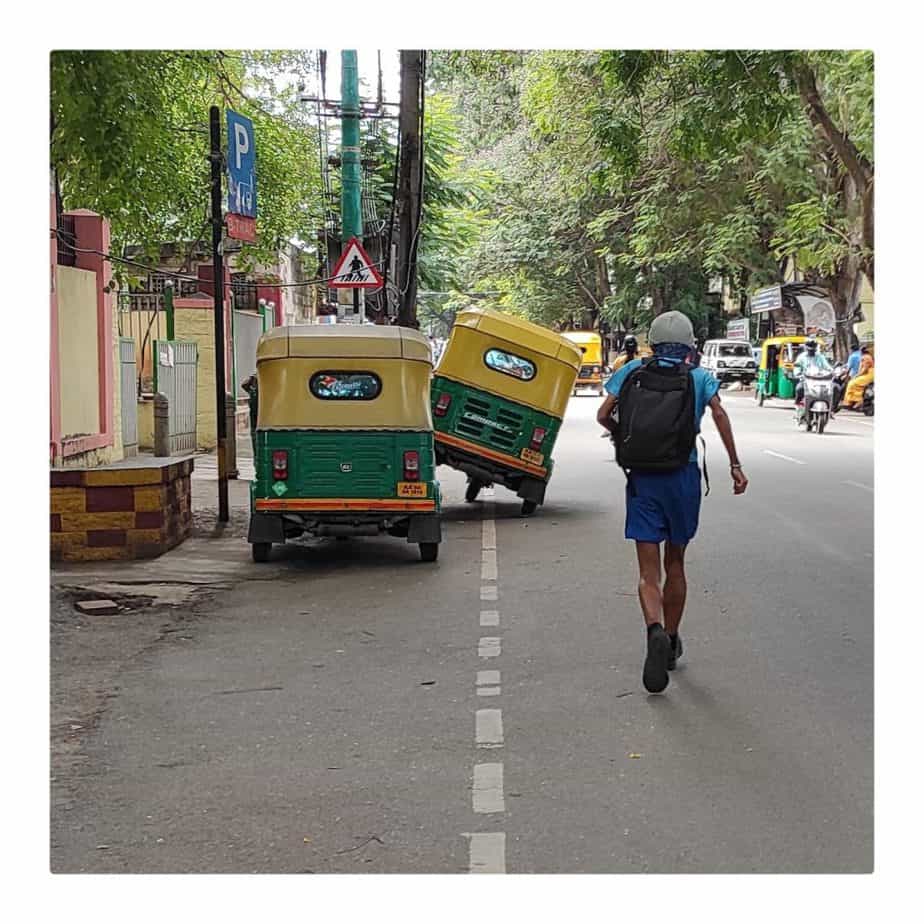
Common issues faced by pedestrians that expose them to higher risks are illustrated in the series of images below.
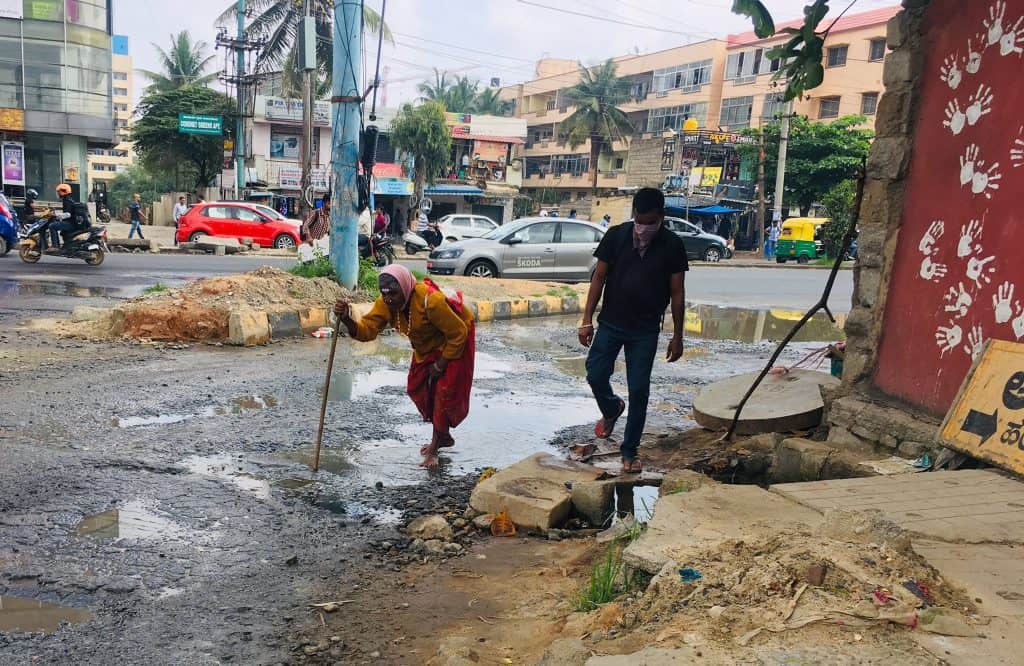
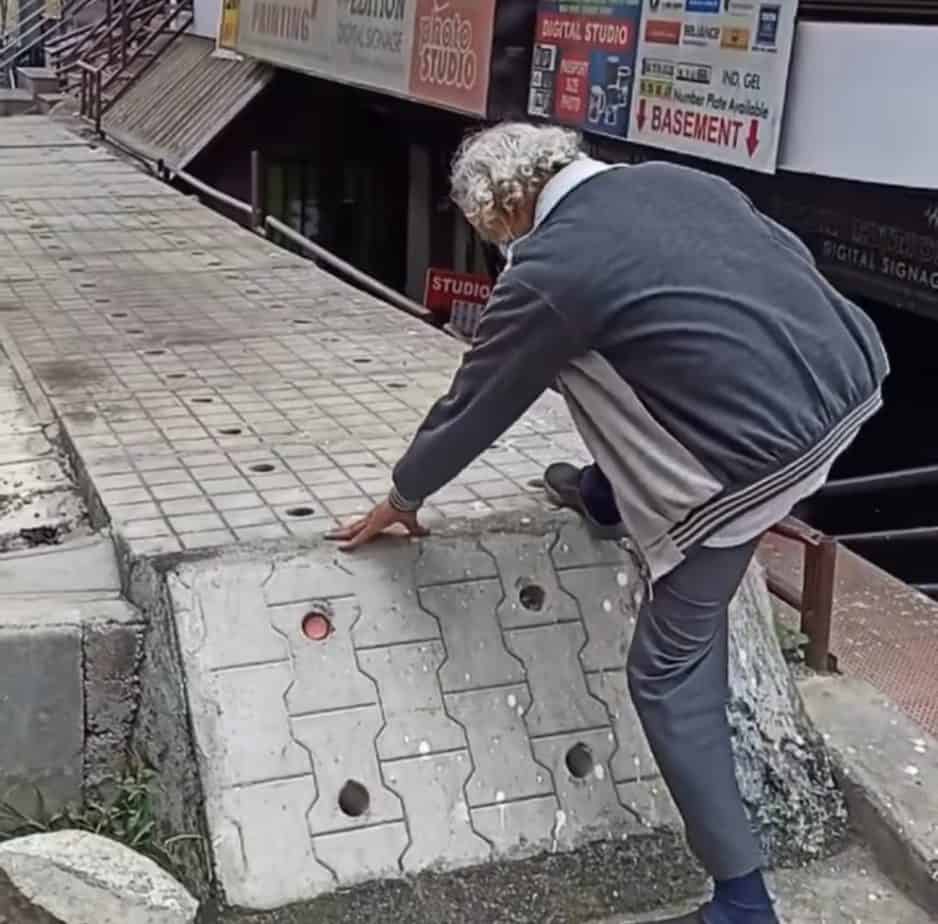
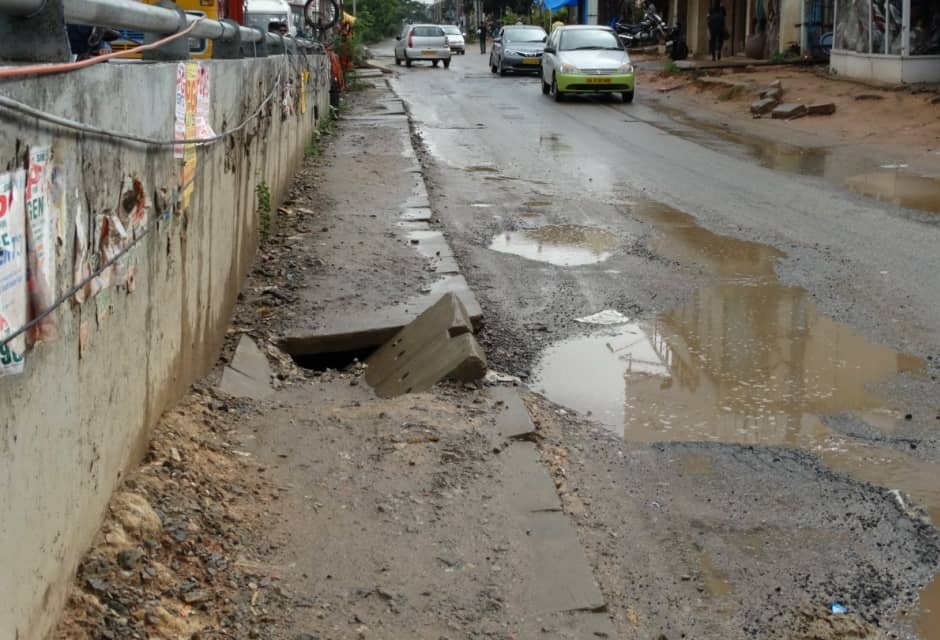
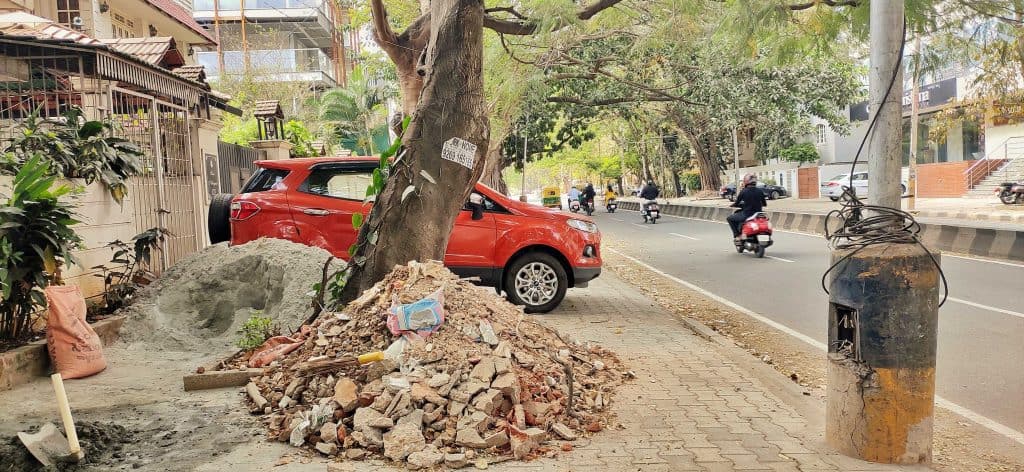
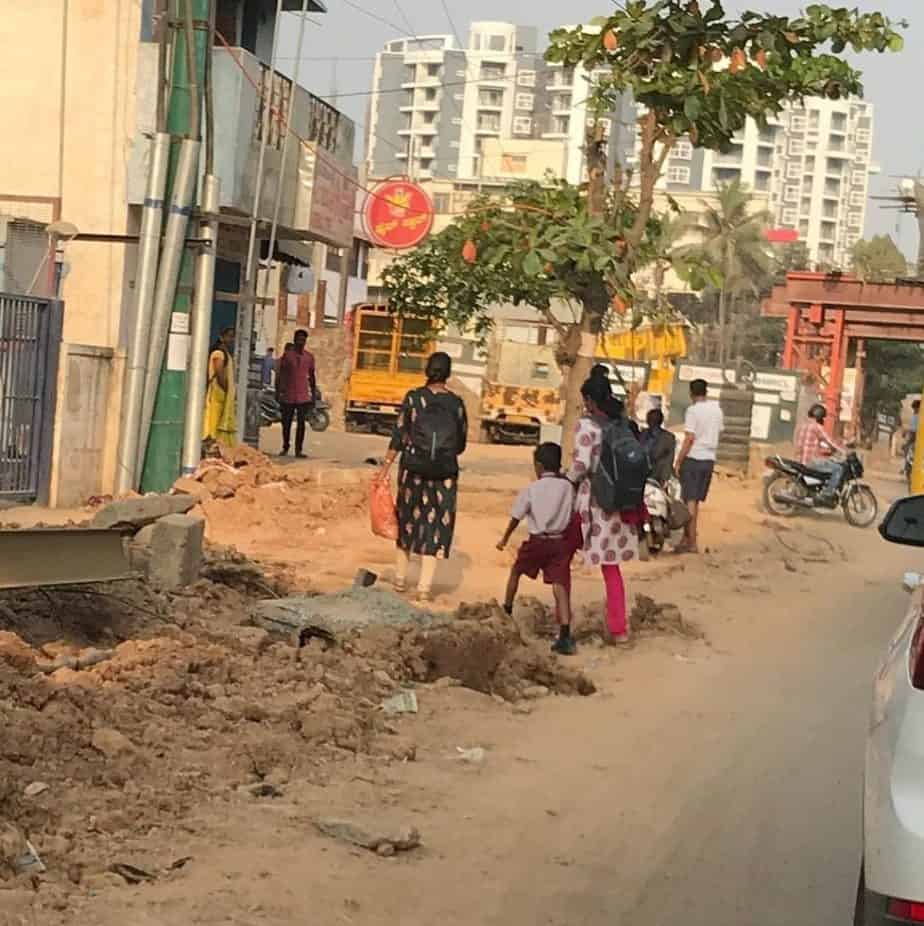
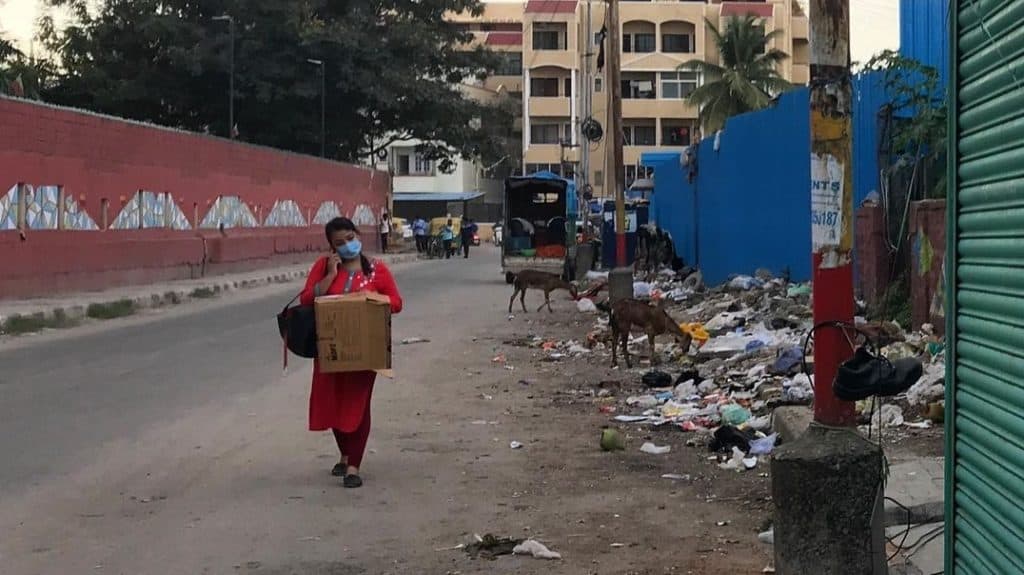






In addition, infrastructure failures like inactive traffic lights and inappropriately-timed crossing signals, lack of space for boarding and deboarding vehicles, no wayfinding and pedestrian navigation systems, and lack of street lighting at night, make pedestrians more vulnerable. Motorist behaviour such as riding on footpaths during peak traffic and constantly honking at pedestrians who have no place to go, adds to the stress and chaos on the road. The absence of traffic police sometimes leads to uncontrolled and unsafe vehicular movement, which further reduces pedestrians’ sense of safety.
[With COVID lockdowns since March 2020, traffic on Bengaluru roads reduced drastically, and government agencies started implementing pedestrian-friendly projects as well. But did this make roads safer for pedestrians? Are these measures enough? We explore this in Part 2 of this series.]
Yes, it’s v true. Bengaluru is no more a Senior citizens Paradise. My family too shifted from Mumbai,n live in Fraser town, ward no.78.Alas, it’s no more a Paradise n there are no good roads n FOOTPATHS, u can never see one road, where u can walk from one end to the other – we need to do a no of high jumps n long jumps.Many Apartments, Commercial establishments have converted our FOOTPATHS TO RAMPS,n ofcourse there are VENDORS, Construction materials, debris on all our FOOTPATHS.We don’t get any co operation from our Engineers whatsoever. Can we get justice ??????