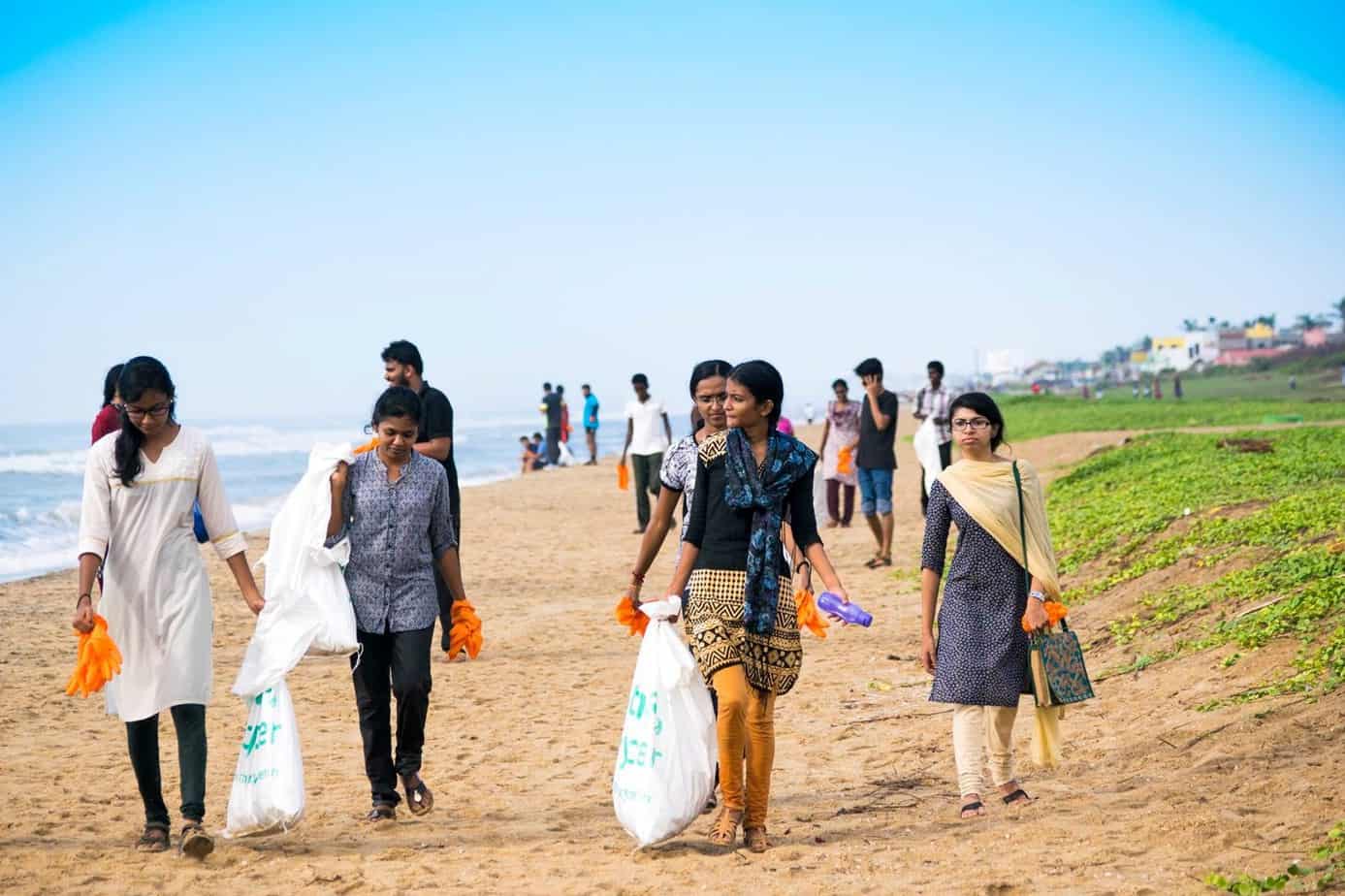
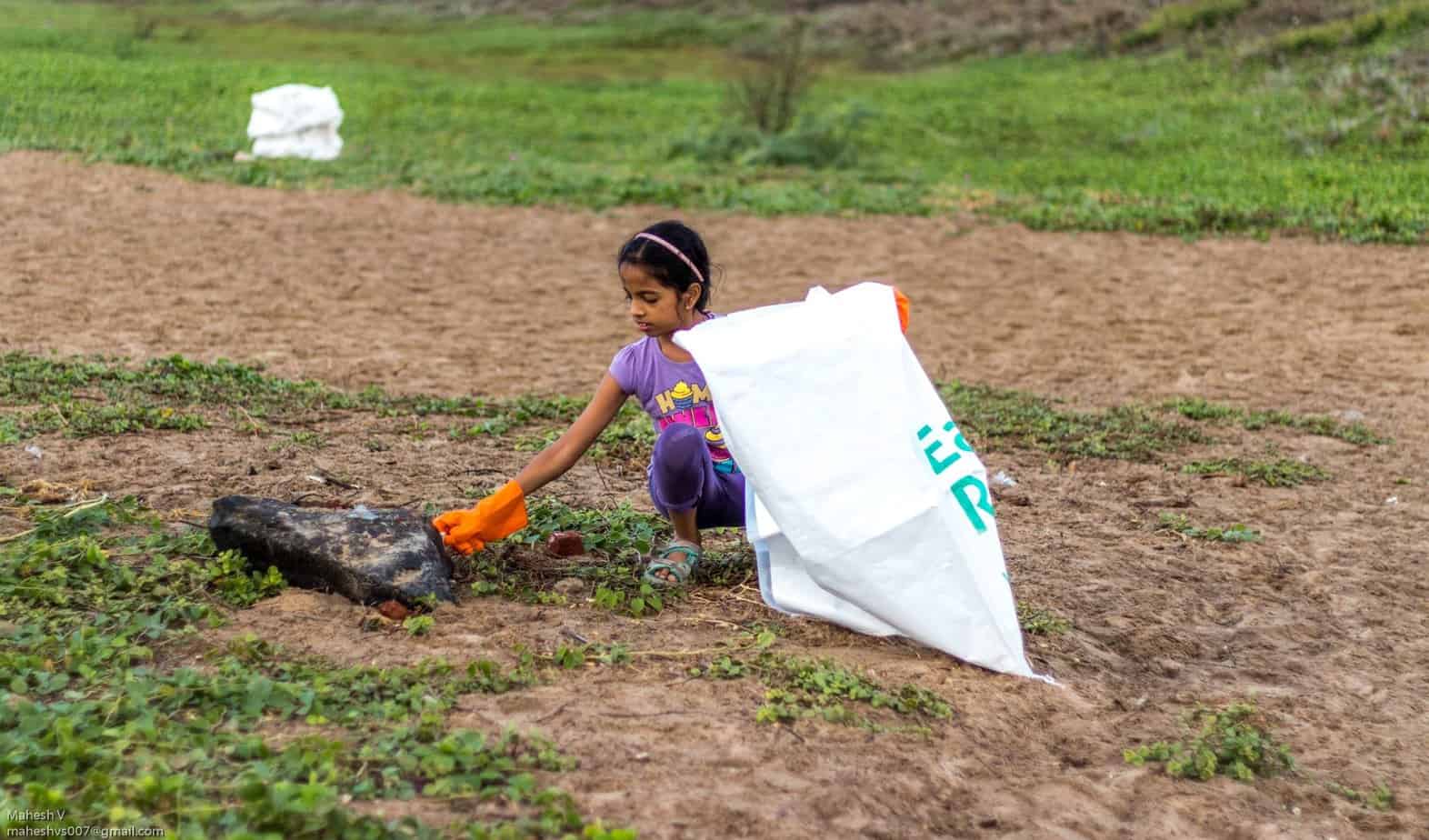
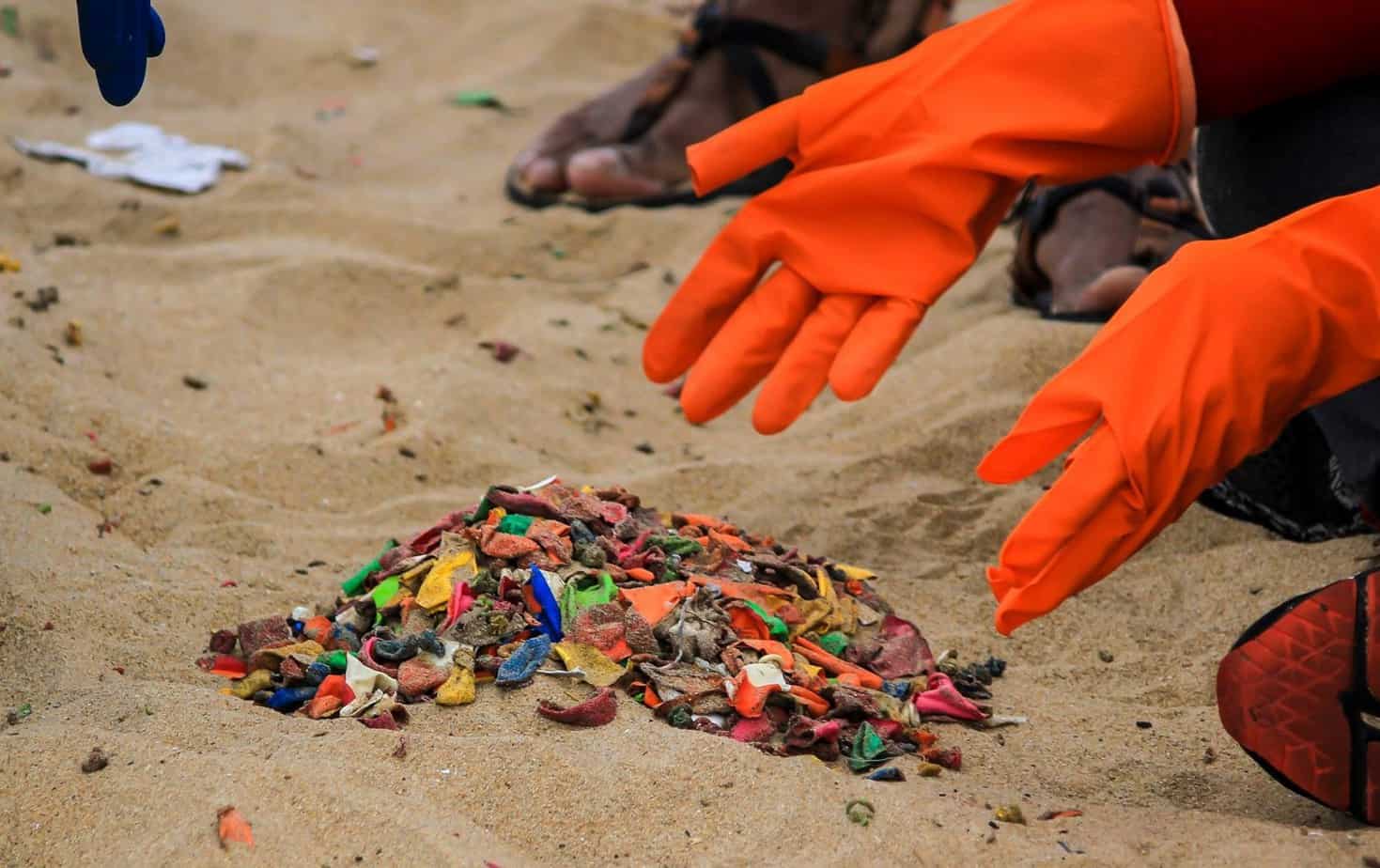
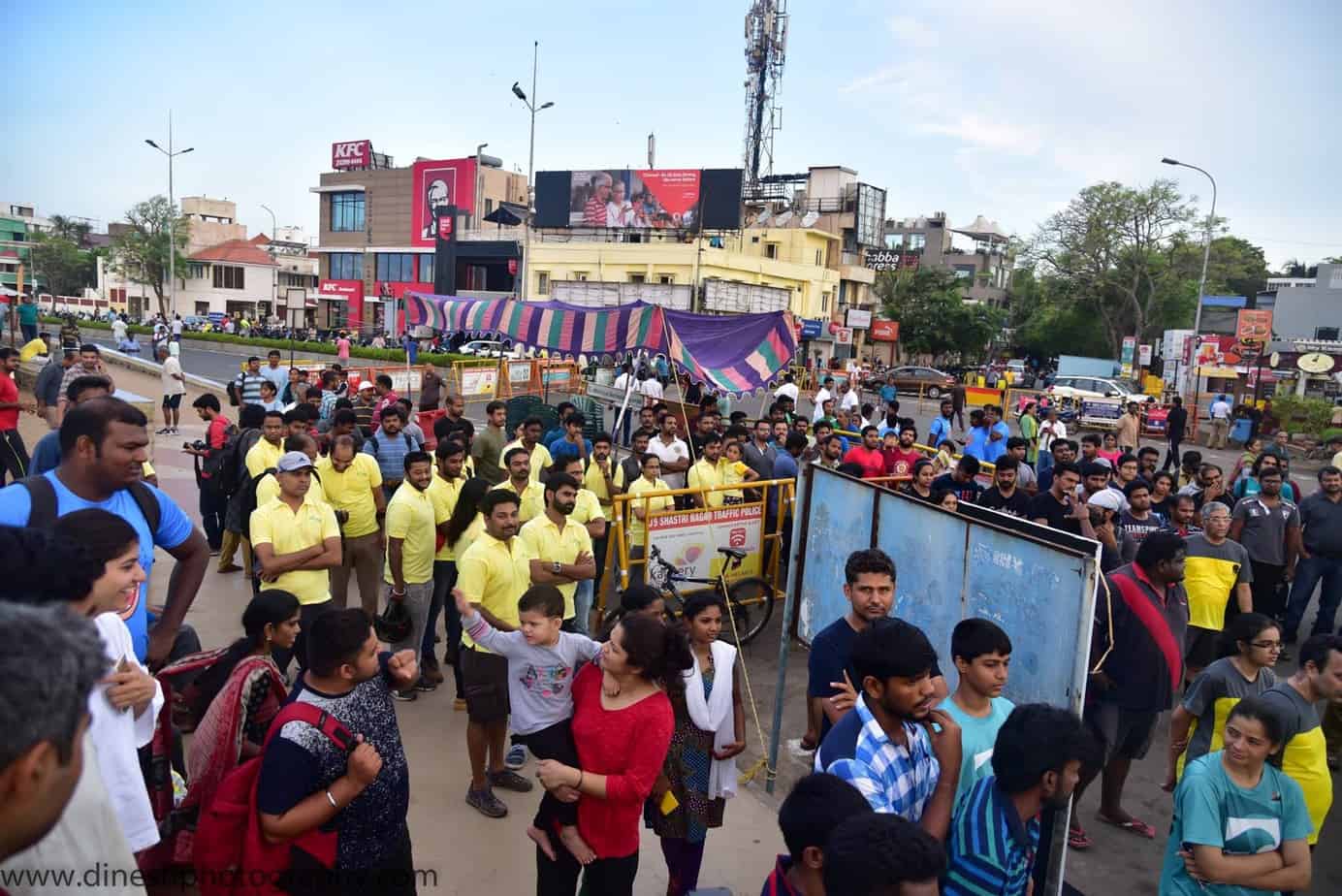
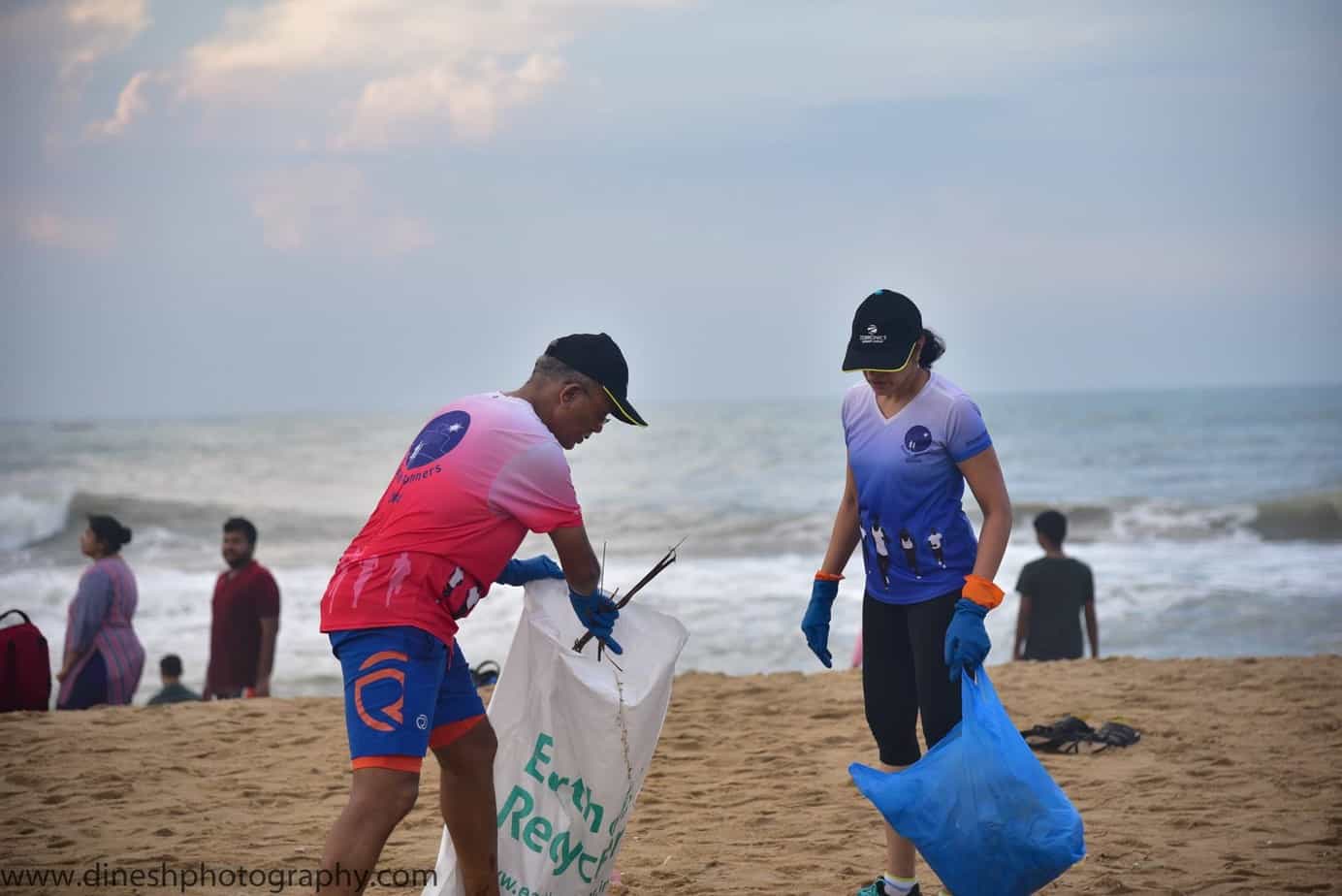
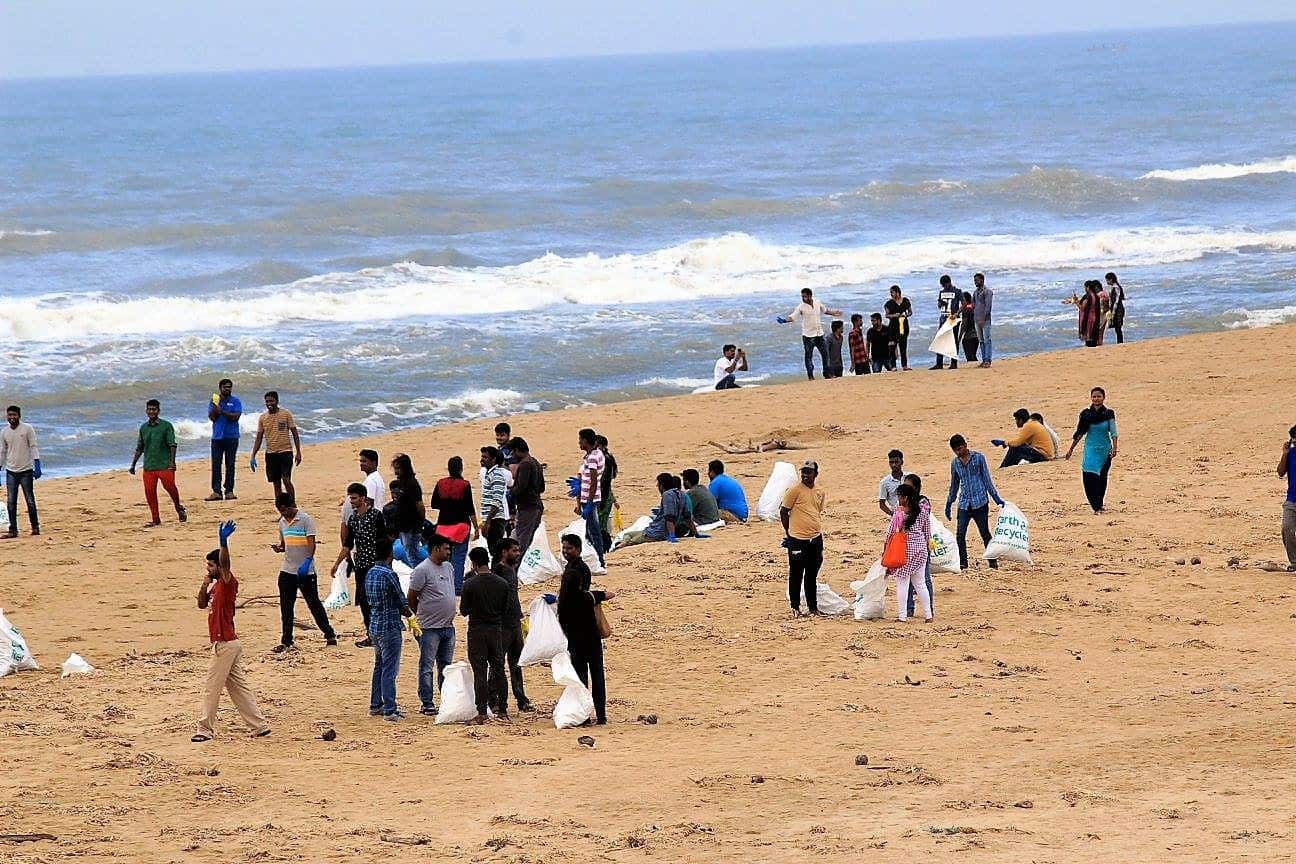
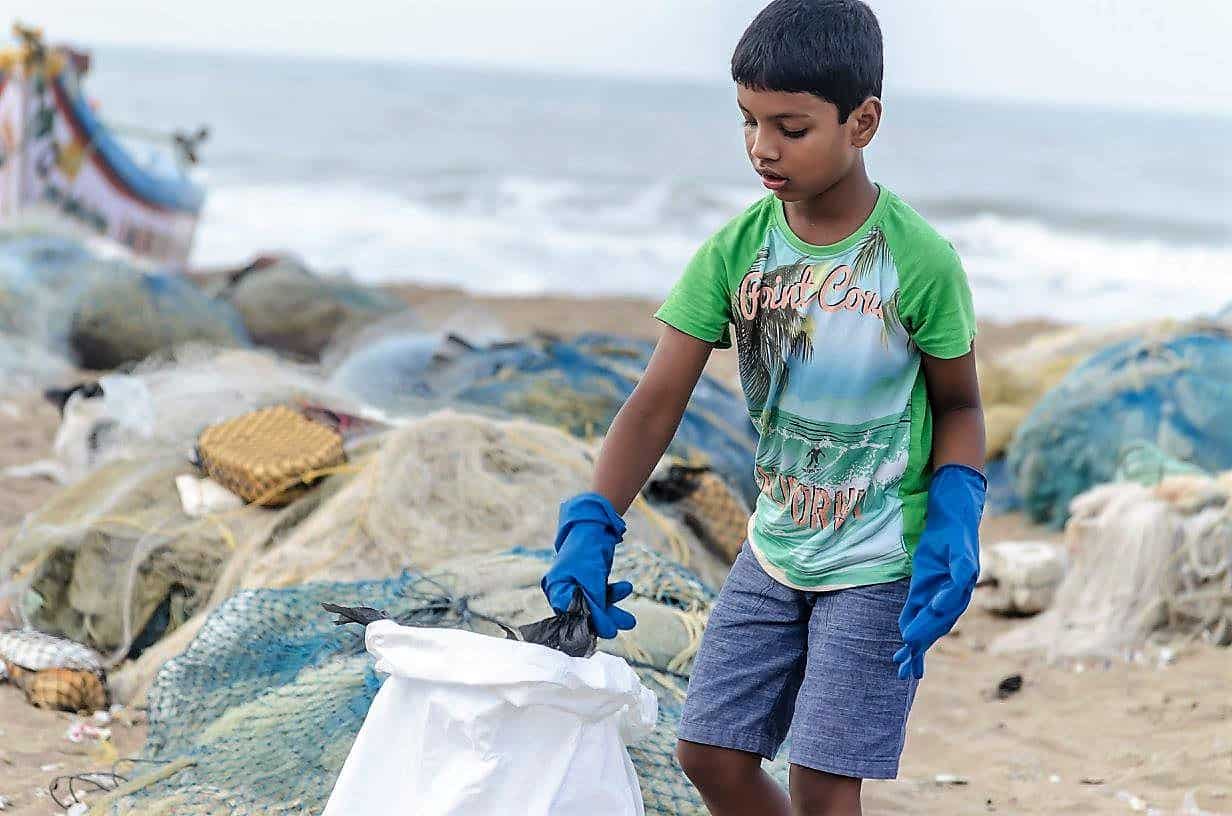
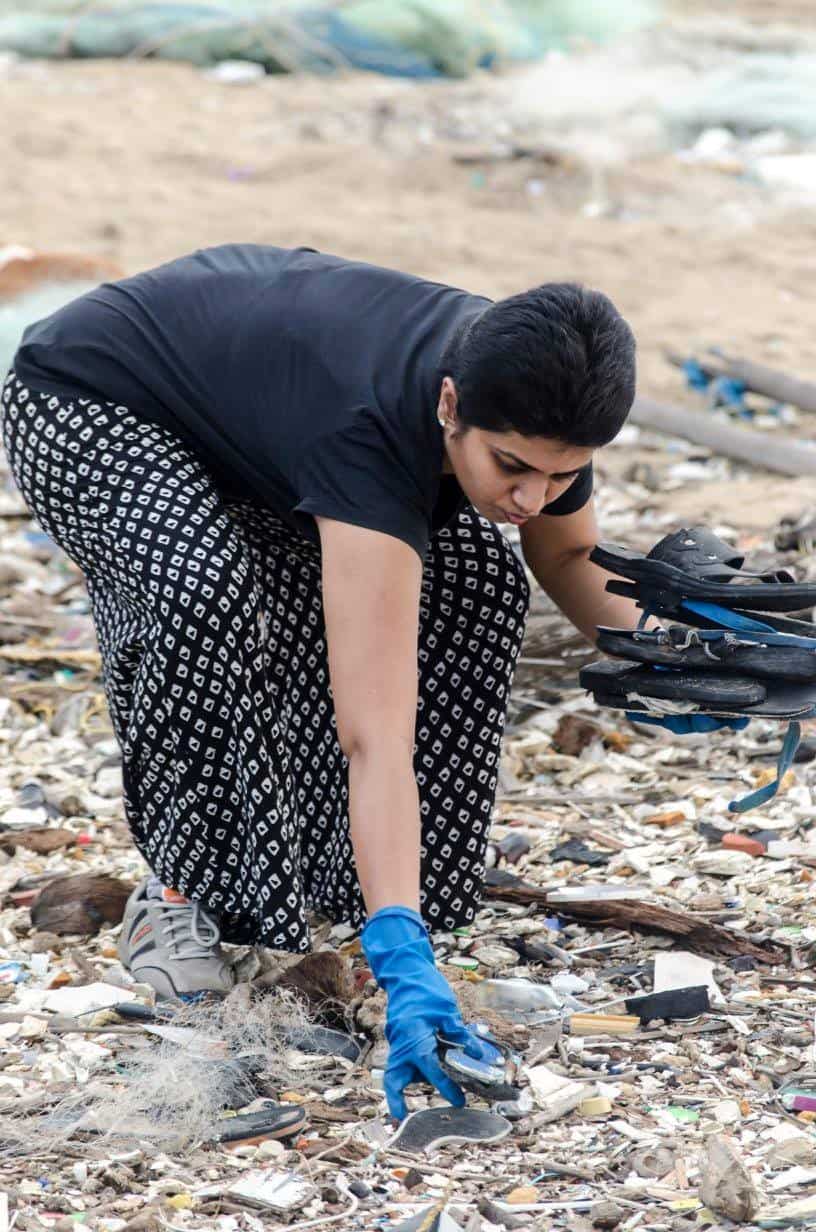
On Sunday, June 18th, Chennai Trekking Club (CTC) and Environmental Foundation of India (EFI) in association with The Hindu and Casa Grande organized the 8th edition of the Chennai Coastal Cleanup (CCC), a South India-wide awareness drive on our growing garbage footprint and the impact on the environment.
5000 volunteers and 130 organizations, schools, NGOs in 10 large cities removed 41 tonnes of garbage from lakes, rivers and beaches.
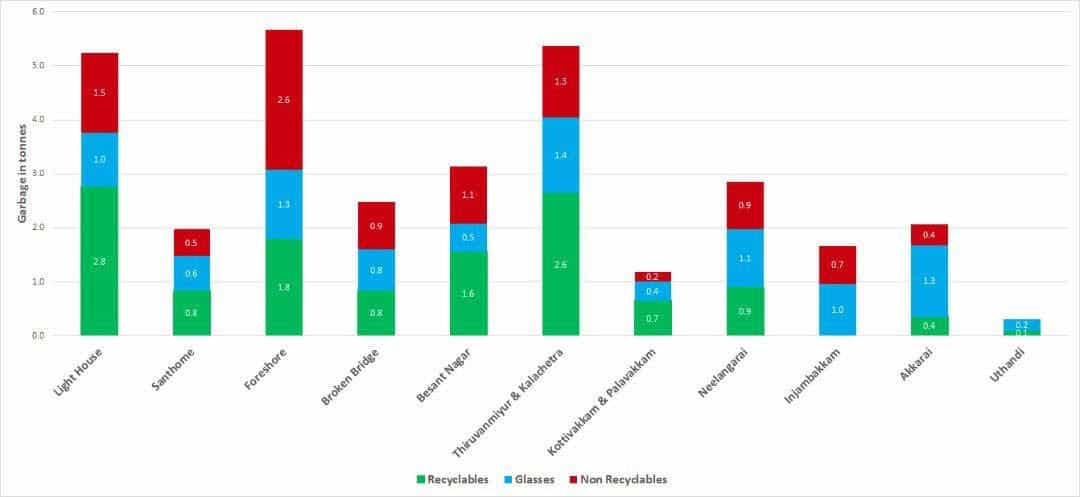
In Chennai, 4600 volunteers participated in removing 32 tonnes of garbage from 20 km of Chennai’s shoreline between Lighthouse and Uthandi. Volunteers segregated garbage in 69% recyclables (glass, plastics, etc) taken by Earth Recycler and 31% non-recyclables (thermocol, chappals etc), which were taken by the Corporation to the landfill.
An additional two tonnes of garbage was removed from two lakes, namely Keelkattalai and Nanmangalam in the city. One must acknowledge the huge support from the Greater Chennai Corporation and Greater Chennai Police that made this event such a success.
Here are a few snapshots of the event that capture the zeal and enthusiasm of all volunteers, young and old: