The existing state of urban biodiversity, environment and natural heritage in Bengaluru is a matter of urgent concern. The impacts of ecological degradation is already felt in the city – for example, monsoons are often accompanied by the grim news of many areas getting flooded. Many of these vulnerable sites are found in large layouts and real estate projects that are built in valley zones and adjacent to lakes/rajakaluves (primary stormwater drains).
A favoured market for the real estate sector, Bengaluru has witnessed an increase in built-up area that has replaced its green cover and wildlife habitats.
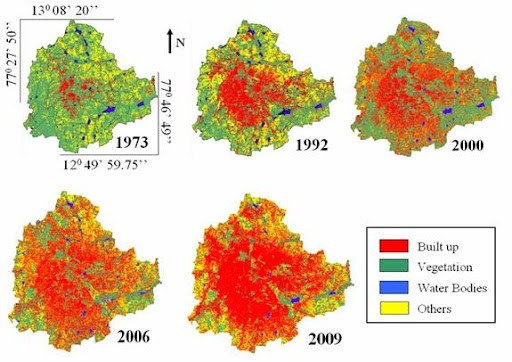
Clearly, construction projects in the city are worsening pollution and exacerbating climate change. So it is worth examining whether the processes designed to mitigate these effects are working as intended.
Depending on the size of the project, a real estate developer is supposed to submit an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) report or an Environment Management Plan (EMP), to get approval. A project with built-up area of 20,000 sq m or more needs to get an Environment Clearance (EC) , along with other permissions from the BBMP, BWSSB, etc. The State Environment Impact Assessment Authority (SEIAA) is the agency responsible for giving EC to projects in Bengaluru.
Read More: Not just Lalbagh, your small neighbourhood park too can protect Bengaluru’s biodiversity
Vidhi Legal and BIC, in collaboration with Citizen Matters, is organising a webinar which tries to bring out the framework of EIA processes in Bengaluru, how these processes work, and why they have not been effective. (Citizen Matters had recently reported on the standard copy-pasting of information in forms that developers submit as part of EIA process.) And given this background, what impact would the Centre’s proposed changes to the EIA notification entail?

Read more: Unchecked tree loss is wiping out the Slender Loris from Bengaluru
Event details:
Event title: Green or gone? Development projects and their impact on environment
Date: February 11, 2022
Time: 6 pm (The webinar will be followed by a brief Q&A session open to participants.)
Register here: https://bit.ly/Green-or-Gone
Speakers:
- Dr K C Jayaramu: Ex-Chairman, State Environmental Impact Assessment Authority, Govt. of India
- Ulka Kelkar: Director of the Climate program, World Resources Institute India.
- Mohan S Rao: Environmental Design and Landscape Architecture professional
- Bhanu Sridharan : Independent journalist
- Moderated by Meera K, Co-founder of Citizen Matters