On October 3rd, Citizen Matters hosted a tweet chat on water supply in Mumbai with Sitaram Shelar and Purva Dewoolkar. The discussion covered how water is sourced in the city; the condition of lakes, the treatment plants, and reasons for water shortage.
Sitaram Shelar is the Convener of the Pani Haq Samiti. He is a member of the core committee of the Hamara Shaher Mumbai Abhiyan and has initiated the 51 Mumbaikar campaign. His work has focused on youth development, governance, poverty and the built environment.
Purva Dewoolkar is a SEED funded PhD Scholar at the University of Manchester. Her research investigates the processes of negotiations and struggles through which the sanitation infrastructure is produced in Mumbai, India.

Mumbai gets its water from a complex network of pipelines, tunnels, balancing reservoirs, pumping stations and lakes. Despite being one of the world’s largest water supply networks, why does Mumbai still struggle with water supply? These questions led the conversation.
The first question was about water demand and supply. How much water does Mumbai need and how much does it get?
“‘Need’ has various calculations, one of them being MCGM claims to calculate as per the Chitale committee report: 240lpcd” said Sitaram Shelar.
Is there a disparity between how much water the rich get as compared to the poor? and how far are we from getting WHO recommended water supply per capita, which is 135l per day? Were additional questions asked.
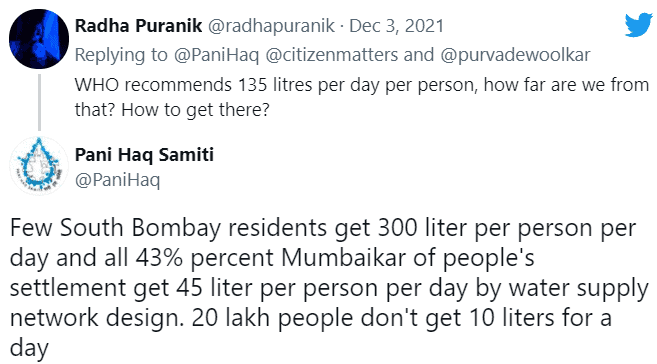
“Mumbai sources around 4175 megalitres of water per day, and 100% of this is from the dams” said Sitaram Shelar. But, are we utilising all our resources?
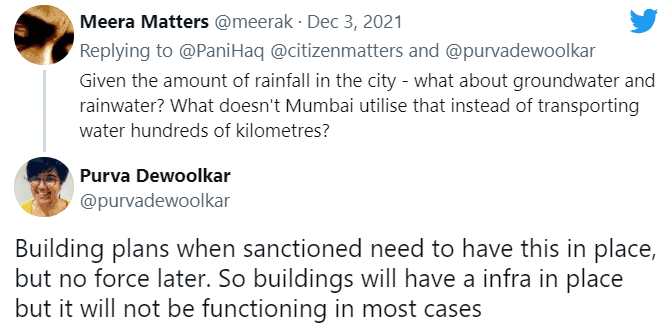
The second question was on how Mumbai sources water and how it is carried into the city.


Water, however, remains more contaminated in some parts of the city like Dadar, Dharavi, Sion, Goregaon and Mulund according to the BMC’s water contamination report of 2020-21.
Is there a regulated rate of water? Who is paying how much for water?

The fourth question asked if we are implementing any regulations to conserve water, is there incentive for good work, or penalisation for bad work?
“Dubious activities like filling ponds to create land, Constructing roads around the existing lakes are some examples of misuse of water resources” said Sitaram Shelar.
Read more: An apartment complex saved 187 houses from going dry

According to Sitaram and Purva, citizens’ constructive and consistent engagement, awareness about water sustainability and political will are the only ways to make clean water equally accessible to all.
