Bengaluru’s water story is full of paradoxes. After all, this is a city where even a lake catches fire. A few hours of rain can wreak havoc on the city. However, come summer, the city faces acute water shortage.
It’s not even Bengaluru alone.
The Delhi Jal Board (DJB) and the Census 2011 numbers indicate that Delhi meets the water requirement of 82% of its households (population: 17 million). However, the same census numbers show that only 51% of slum-households in Delhi have access to water within their premises. The average level of ground water exploitation in Delhi is 137%, with tanker supply being a critical lifeline. DJB operates around 800 water tankers; however, the supply is quite expensive and therefore, limits access.
Mumbai, which is home to 12.5 million people (2011 Census), supplies water collected from lakes and stored in 28 service reservoirs. Around 76% of households have access to piped water supply (average per capita supply: 279 lpcd); only legal slums have water supply connections, while non-notified slums are dependent on informal water distribution systems such as ground water.
However, the ground water in Mumbai is not fit for consumption and the corporation bans use of water from wells and ponds. When water-stressed, however, many households have no other option but to use ground water.
Cities across India are facing acute water shortage. According to a Service Level Benchmark study of 28 cities (14 states), the average daily supply is just 3.3 hours a day. Only two of the cities surveyed (Chandigarh and Trivandrum) received water for over 12 hours (even this was limited to 62% of the urban households that have access to treated tap water).
Against the benchmark of 135 litres, the per capita supply of water averaged at 126.4 litres per day. This too varies significantly across the cities surveyed. A National Institute of Urban Affairs study suggests that nearly 41% of the country’s 115 Class-2 cities (population: 50,000-1,00,000) and 22% of Class-1 cities (population 1 lakh-10 lakh) received, on average, less than 70 litres of water per capita.
Non-Revenue Water (NRW) or unaccounted-for water is high in Indian cities because of outdated water systems, illegal connections, leakages, poor maintenance and lack of proper mapping of the distribution system. The average NRW in India is between 30 to 50%.
Clearly, there is a gap in our management of water and the solution may lie in reconsidering how we look at water flow.
What is the solution?
A simple ‘Water Flow Diagram’ (WFD) can help understand the complete water cycle and help change any sub-optimal usage and management. A WFD helps visualise the source, supply and consumption of water as well as the volume of waste-water generated, recycled, reused and returned to the environment.
At the Center for Study of Science, Technology and Policy (CSTEP), the process of preparing a WFD for Bengaluru city helped us identify numerous discrepancies.
For instance, although the city consumes approximately 3600 MLD (million litres per day) of water, the water supply board (BWSSB) provides only 2130 MLD (1380 MLD from the rivers and 750 MLD from groundwater sources). The remaining sources of water are unaccounted for (includes illegal borewells and private water supply).
Of the 3600 MLD consumed daily, only 520 MLD of the resulting waste-water is treated and just 49 MLD of the treated wastewater is reused. This implies that while we use large amounts of water from the environment, very little actually goes back to refurbish the supply.
BWSSB pumps water from the Cauvery river (located 100 km away) and Arkavathi river (located 25 km away). Back home, however, lakes are converted into stadiums and bus stops, or polluted with sewage and industrial waste— in other words, water is wasted.
How does a Water Flow Diagram help?
Civic authorities, and especially citizens, approach water from a supply point of view. That is, they view water as a resource extracted from a source (river, lake, groundwater, etc.) and then supplied to households by the municipality or private parties. This is often where the cycle ends, and it fails to take into consideration how much water goes back to the ecosystem and how.
A WFD aids in creating water balance in the city by identifying how interventions at one or more stages of the water cycle affect other stages or the entire cycle itself. For example, interventions like rainwater harvesting, even if done at an individual household level, can help address water deficits in the city.
A report by the Institute of Social and Economic Change, titled ‘Rainwater Harvesting Initiative in Bangalore City: Problems and Prospects’, reported that an estimated 4 crore litres of water can be collected per year if RWH is adopted on one acre of land. Thus, if RWH is carried out for the entire city, significant volumes of water could be collected annually.
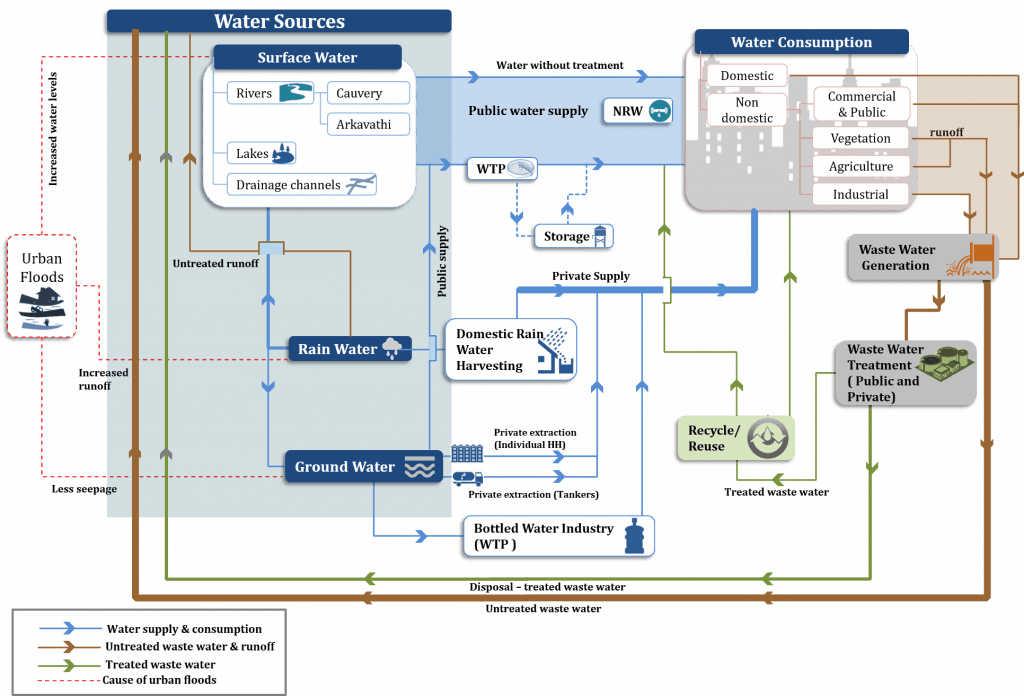
The Water Flow Diagram for Bengaluru demonstrates how water flows from source to consumer; more importantly it closes the loop by showing how waste water (treated as well as untreated) goes back into the water cycle. Pic: CSTEP
The WFD can also help planning authorities understand the quality of water supplied, the cost incurred in supplying water to the people and the energy utilised at each stage of the water cycle.
For example, by overlaying the cost layer on a WFD, we may see that the cost of extraction and transportation from a distant water body is actually higher than the cost of treating and reusing wastewater. The WFD will thus help make policy-makers aware of the actual cost incurred in supplying water, including the social costs incurred by inaction.
Identifying gaps in the water cycle of Bengaluru enabled CSTEP to make targeted suggestions towards plugging gaps in the city’s water cycle. One immediate observation was the lack of data for various stages of the water cycle. Moreover, the available data was often inconsistent.
While mapping the responsible government agencies, it was observed that different agencies managed different stages of the water cycle, without any coordination among themselves. Thus, CSTEP’s policy analysis for Bengaluru recommends an integrated approach to water management. The think tank specifically recommends that different agencies managing the water cycle be brought together, when planning for the city’s infrastructure development (e.g. when creating a Master Plan or the City Sanitation Plan etc.)
Preparing a WFD for Bengaluru also demonstrated the need for looking at water as a complete cycle across cities and villages in India—such an outlook would allow us to fill in the missing gaps in understanding water availability, supply and demand as well as reuse options.
If we want to ensure adequate water availability in our cities without threatening natural reserves, the urgent and essential step is to complete the loop for water data and plug all avoidable gaps.