Those tagged as ‘encroachers’ are the victims of the historical marginalization process, says Founder of Chennai-based NGO Information and Resource Centre for the Deprived Urban Communities (IRCDUC) Vanessa Peter. A study by the NGO reveals that limited access to basic facilities, especially during the pandemic, has increased the existing vulnerabilities of the communities who are grappling with the adverse impacts of resettlement.
Life on the margins
The report titled ‘Life on the Margins – Access to Basic Infrastructure Facilities in the Resettlement Sites of Chennai’ points out several key issues pertaining to living conditions at resettlement areas. It has been curated based on field visits and interviews done by a team of student researchers trained by IRCDUC, along with community leaders from the settlements.
The study was conducted in five resettlement sites — Perumbakkam, Semmenchery, Gudapakkam, Navalur and All India Radio (AIR) Site, with an objective to identify both site-specific and common issues faced by the resettled families.
As part of the study, the team has also proposed specific recommendations to address the critical issues of resettlement in the aforementioned sites and to further strengthen the Resettlement and Rehabilitation (R&R) Policy evolved by the government. In addition to being uprooted from places where they lived for decades, those being ‘resettled’ by the government are not given a place to call it a ‘home’, the key point noted by the study.
Read more: Why COVID proved to be a greater challenge in Chennai’s resettlement colonies
Forced evictions the norm
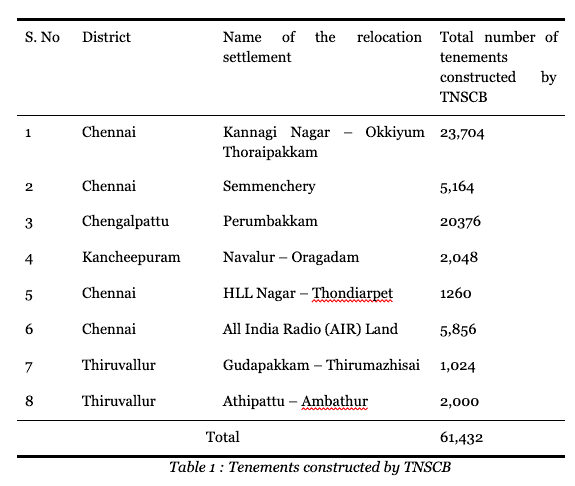
According to the data furnished by the researchers, 61,432 families comprising 2.5 lakh individuals from Chennai residing in settlements inside the city were forcibly evicted in the last two decades and resettled in eight resettlement sites located in the peripheral areas of the city. Most of the resettlement sites constructed till date are either in low-lying areas prone to flooding or in isolated and remote locations inaccessible to the resettled families.
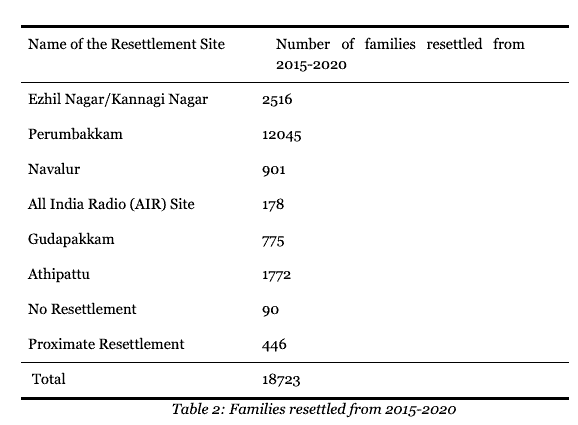
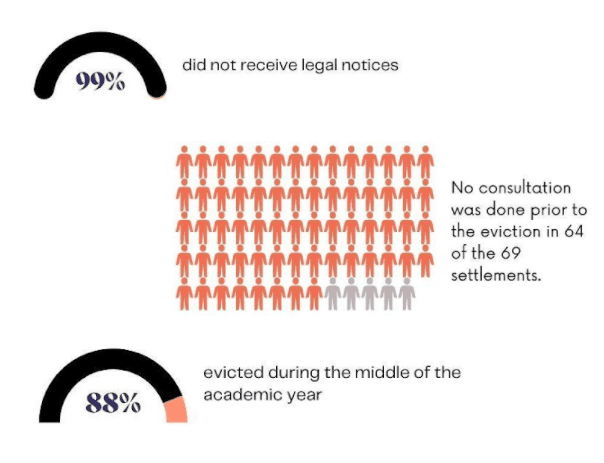
As many as 18,723 families comprising nearly 75,000 individuals from 69 settlements were reported to be evicted from their houses in the five years between 2015 and 2020. The families were subsequently resettled in Perumbakkam, Ezhil Nagar/Kannagi Nagar, Navalur, Gudapakkam, AIR Site and Athipattu. The city was subjected to some of the most massive eviction drives of all times, since the December floods in 2015.
However, it is to be noted that of the 18,723 families who were resettled, 90 families were not provided with alternative housing facilities and only 446 families were given houses in a proximate location.
Victims of marginalization
Vanessa Peter said that after every natural disaster there is a massive eviction and the blame is put on the so-called ‘encroachers’. “These people are the victims of the historical marginalization process who have migrated over a period of time and settled in a place because they had no other option. They do not have any economic gain out of these settlements. Tagging them as ‘encroachers’ and forcibly evicting them, without exploring the alternatives, only leaves them with loss of livelihood, shock of eviction and resettlement,” said Vanessa.
Government of Tamil Nadu is about to complete the construction works of 6,877 tenements near the Ennore Thermal Power Plant. On November 2018, 26.68 acres of land belonging to the Tamil Nadu Housing Board in Ennore was reclassified from ‘Special and Hazardous Industrial Use Zone’ to ‘Residential Zone’ by the Chennai Metropolitan Development Authority (CMDA). This was done even after a representative from the Tamil Nadu Pollution Control Board (TNPCB) expressed concerns over the possible pollution due to the nearby Thermal Station and its impact on the residences to be constructed under the development plan.
Further, the resettlement site of Perumbakkam (with 1,152 houses) is also being expanded under the Global Housing Technology Challenge without rectifying the existing pitfalls in the resettlement practices.
Read more: COVID-19: Women, children in low-income housing bore the worst brunt
Draft R & R policy falls short
“Though it could be argued that Ennore has better connectivity than other sites, it is a hazardous zone. The existing sites are living examples of patterns in resettlement issues. However, when the government came up with the draft of R&R Policy, it failed to address some of the critical issues,” said Vanessa, adding that the study highlights the key issues that have to be looked into while framing the policy.
A report in this regard has been submitted to the government and the team is looking forward to the final version of the R&R policy.
With an elected municipal council in place, Vanessa believes that some of these issues could be resolved as the residents would have more leverage in demanding their needs to the elected representatives.
However, she pointed out that not all the resettled sites fall under the jurisdiction of the local bodies. “Various departments are involved in providing the basic amenities and they should be held accountable for it. This is where the role of a high-level committee, headed by the Chief Secretary to Government with Secretaries to Government as members, that was formed in 2011, holds significance. This committee was set up to resolve issues pertaining to basic amenities and social infrastructure in the resettlement sites,” she said.
[In Part II of this article, we shall look at more detailed findings of the IRCDUC report on various aspects of life in the resettlement colonies.]