At the recently held BBMP – Work Orders, Budgets and Processes Datajam, a group of citizen volunteers analysed the data available in the public domain. Here are their observations and suggestions on BBMP’s expenditure and efforts in waste management.
To:
Dr. Harishkumar,
Special Commissioner (SWM)
Dear Sir,
We are a group of citizen volunteers who would like to share our observations and suggestions on BBMP’s expenditure and efforts in waste management.
Solid waste management constitutes 14.7% of the BBMP budget (1643.72 crores). As part of the Shubra Bengaluru Project, BBMP has identified 1,555 Garbage Vulnerable Points (GVPs) also called as ‘black spots,’ in the city. Of these, 1,479 (95%) are categorised as ‘evening spots,’ and 76 perennial spots. To monitor these black spots, BBMP installed 2,415 CCTV cameras at an estimated cost of Rs. 22.32 crore. In 2018, BBMP has spent Rs. 20 crore to install more than 2,500 CCTV cameras for the same purpose and none of them are in a functioning state.
Using secondary data, we identified that segregation of waste was a major pressure point for solid waste management in the city. Our analysis showed that inner localities like Chickpet and Shivajinagar were doing poorly in waste segregation. However, this is based on 2017 data.
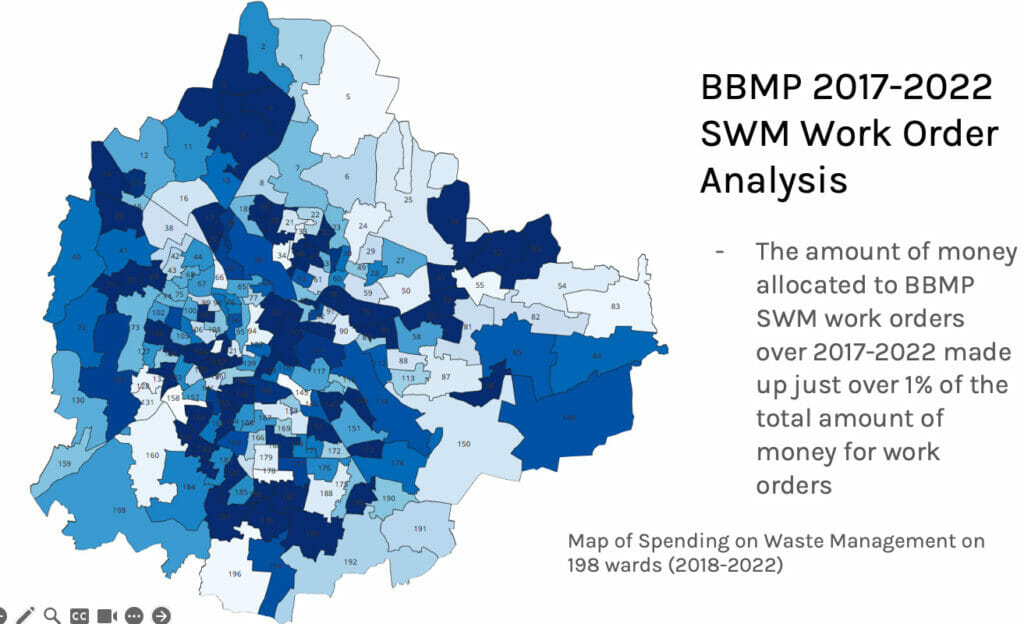
Of the BBMP work orders that were publicly available, only 1% of work orders were made for SWM and the expenditure was also uneven across the wards. (Note: This analysis is based on work order data available on the BBMP site. It is not complete or comprehensive.)
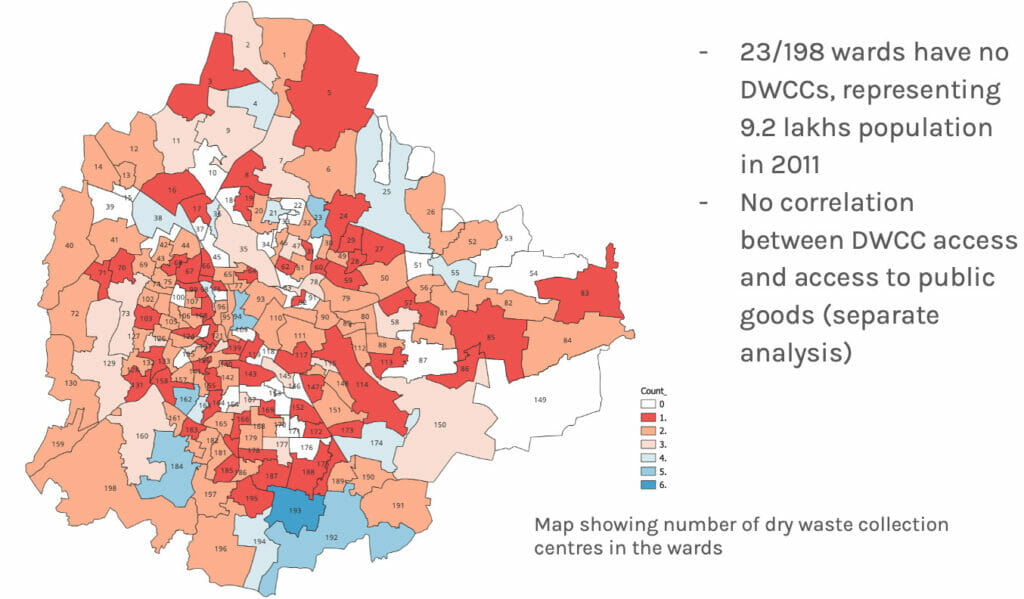
The team also found that Dry Waste Collection Centres (DWCC) were unevenly distributed across the city, with 23 of 198 wards having no DWCCs.
Suggestions:
- The latest data on segregation needs to be made publicly available
- At least 50% to 55% of municipal solid waste is also a valuable resource, which can be recovered profitably using different technologies through following processing options
- Organic fraction of municipal solid waste contains biodegradable matter ranging from 30% to 55%, which can be profitably converted into useful products like compost (organic manure), methane gas (used for cooking, heating, lighting, production of energy) etc. through the following processes
About us:
We are volunteers who participated in a recent OpenCity data jam – civic solutions workshop. The datajam was organised by OpenCity, a civic tech project that helps make public data on cities accessible to all. Our goal is to enable citizens and civic groups to have a shared understanding of their city’s issues and use data as a basis for co-creating solutions. At the event on July 15th, we looked at BBMP work orders, budgets and processes.
More about the event can be found here.
Report compiled by Bhanu Sridharan
Also read:
- What does it mean to live near a solid waste dumpyard in our cities?
- Opinion: Five areas Swachh Bharat 2.0 must focus on to overcome our real waste challenges
- Solid waste management: BBMP budget prioritises the worst solution of them all, more landfills
- How has Bengaluru fared in empowering waste workers?
Collection, analysis and delivery of data’s serve no purpose unless the civic authorities are made to implement it’s plans and programs based on data’s.