‘Poison in the Air’, a study by Chennai Climate Action Group (CCAG), has revealed that six major industries in the Ennore-Manali region have been contributing to pollution during 59% (215.35 days) of the previous year (2019).
The study analyzed over 18 lakh hours of the stack emissions data of TANGEDCO’s North Chennai Thermal Power Station (NCTPS) Stage I, NTECL Vallur power plant, Chennai Petroleum Corporation Ltd (CPCL), Tamil Nadu Petroproducts Ltd (TPL), Manali Petrochemicals Ltd (MPL), and Madras Fertilizers Ltd (MFL) obtained from Tamil Nadu Pollution Control Board’s (TNPCB) Care Air Centre through the Right to Information (RTI) Act.
According to the rules, these industries, that fall under the red category, are mandated to monitor their stack emissions on a real-time basis, and share emission levels instantaneously with the TNPCB for facilitating immediate regulatory measures. However, this norm has been violated and the violations continue unabated.
Industry-specific observations
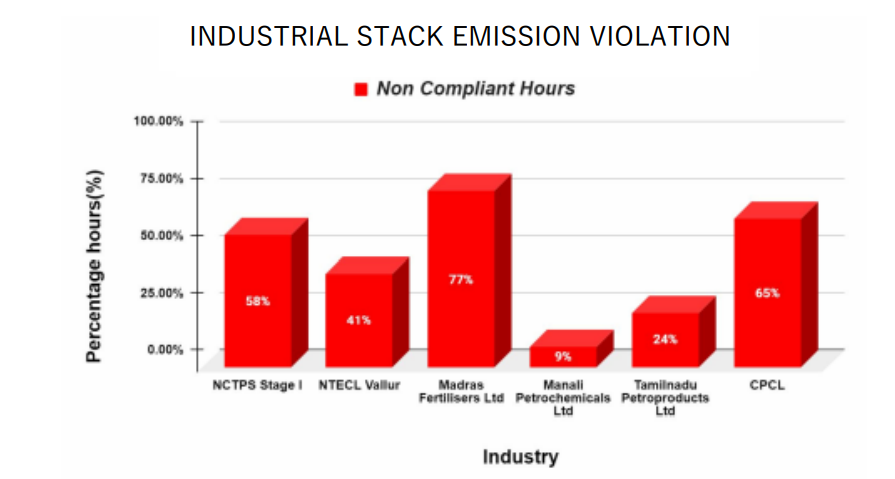
- With a capacity of 10.5 million tonnes per annum, CPCL violated emission standards for 65% of the time in 2019.
- Madras Fertilisers Ltd operated in violation of prescribed air pollution norms for 77% of the year. For 99% of the period, particulate matter emissions were non-compliant. The company also failed to monitor emissions of Ammonia for 71% of the time despite causing frequent ammonia leaks. Similarly, Hydrogen Fluoride (HF) emissions were not recorded for 62% of the time. Like the Bhopal gas tragedy, HF gas leaks can cause widespread destruction if left undetected or if early warning mechanisms fail.
- Public utility TANGEDCO’s NCTPS Stage I violated emission norms for 58% of the year. Unit 1 was non-compliant for 88% of the period.
- NTECL Vallur disregarded emission standards for 41% of the year. Emissions of highly polluting SO2 exceeded permissible limits 82% of the year.
More industries planned
The vast industrial area stretching from North Chennai through Manali to Ennore hosts the city’s largest garbage dump, two coal-fired power plants and their ash dumps, coal stacking yards, a 10.5 million tonnes/year petroleum refinery, dozens of petrochemical industries, fertilizer plants, three large ports and a maze of roads with high traffic of diesel-powered heavy vehicles.
Despite the already prevalent poor air quality and ailing local health, pollution-intensive industrialization is set to intensify in this region. 3000 MW of coal-fired power generation capacity, a plastics industrial estate, a petrochemical industrial township in Ponneri, and a 320 tonnes per annum mega port (nearly eight times the combined capacity of the Chennai Port and Kamarajar Port) are a few of the industries planned for this region. Such developments are bound to drastically worsen the stress on water resources, air quality and health in the region, and expose local residents to a heightened risk of disasters — including floods, gas leaks and vulnerability to various diseases.
Demands of North Chennai residents
TNPCB which has the mandate to prevent and control pollution is dysfunctional, and the Greater Chennai Corporation, which has the mandate to protect public health, is indifferent. Chennai Climate Action Group and children from Zenith Tuition Centre, Thiruvottiyur, and Arunodhaya in North Chennai are reaching out to elected representative, political parties and regulators to reclaim their future and demand:
- An indefinite moratorium on setting up of new industries or expansion of existing industrial activities in the Manali to Pulicat region.
- Region-wide health and environment carrying capacity study to chart out a plan for remediation of the environment, and restoration of health.
- Immediate action against violating industries, including shutting down of repeat offenders
- That TNPCB officials are held accountable for their failure to enforce environmental laws, with a time-bound action plan to make TNPCB effective law enforcers.
- That the Health Officer of Greater Chennai Corporation and other relevant local bodies exercise their responsibilities under the TN Public Health Act to ensure that public health is not affected by the illegal operation of industrial units in the region.
(This article is based on a Press Release by Chennai Climate Action Group (CCAG) and has been republished here with minimal edits.)
It has been known for over twenty years that these industries are routinely flouting PCB rules. Why hasn’t action been taken so far?
Will the present exercise also be equally an eyewash?