The story of Ennore is neither new nor untold. However, there is a need to retell it, only because justice seems to be slipping further and further away. The dual onslaught of unplanned industrialisation and deforestation has taken away an important constitutional right from Ennore residents — the right to life.
Both public and private sector industries have been drastically exploiting the natural resources of Ennore since 1993. Who suffers the consequences? The residents in eight villages of Ennore, for whom clean air and unpolluted water has become an unattainable luxury.
As the locality suffers the consequences of industrialisation in its 25th year, we take another look at the story of Ennore: the visible pollution in the area and how it has been contributing to the loss of livelihoods and impacting the health of citizens.
Nettukuppam is a sleepy locality in Ennore. Geographically, it is the first in Greater Chennai Corporation: Ward 1, Division 1 and Zone 1. However, the deplorable living conditions due to air and water pollution and the absence of amenities such as narrow roads probably makes it the worst among localities in the metropolitan area.
Take a look at the estuary, where Ennore River meets the Bay of Bengal. Located close to the estuary is the North Chennai Thermal Power Station that discharges hot water into the estuary, killing marine life. Few seafood varieties such as River crab, Moulasi and Kodukai that breeds in the estuary face extinction today.
Listen to C Maga, a resident of Ennore. “Nets used to be stacked in my house. At least twenty to thirty people brought in the catch and segregated the fish varieties according to their size,” she recalls nostalgically, “Elders (read fishermen) used to give us some fish as pocket money. We used to barter the fish for snacks such as kottangoochi halwa, sundal and mashed potato. The sight of live prawns delighted us. Today, finding live fish is very rare. We have been forced to a point where we now have to buy fish for money.”
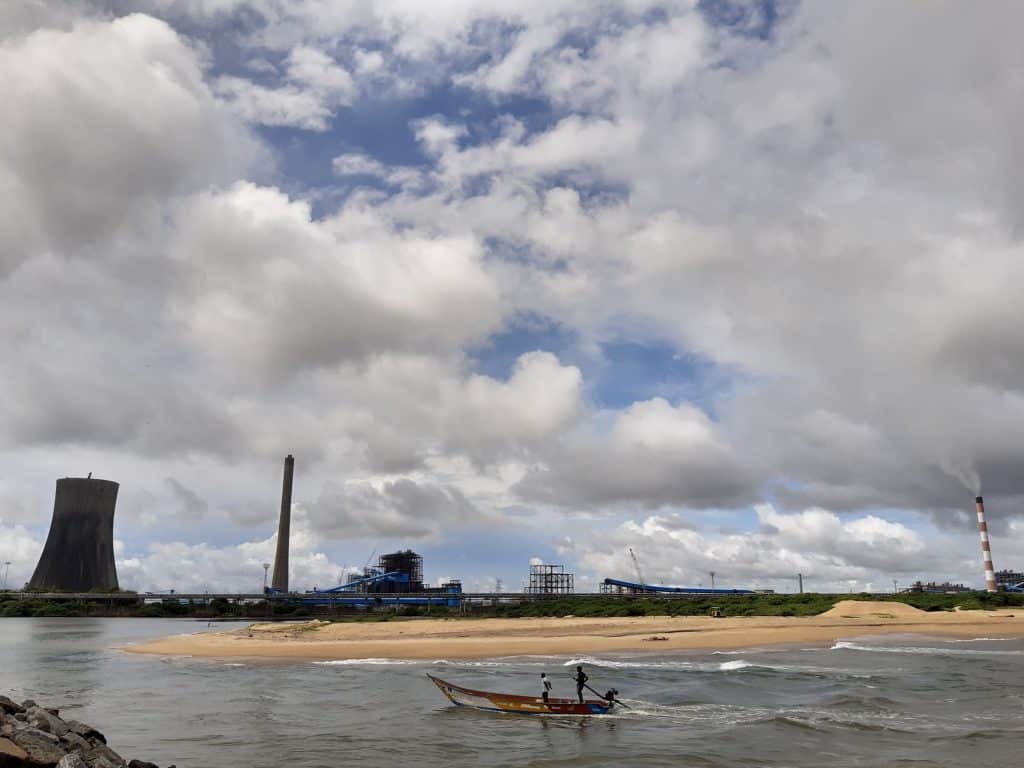 The sea is so polluted now that fishermen have to set sail for more than 20 km for a decent catch. It is a livelihood loss for these fishermen.
The sea is so polluted now that fishermen have to set sail for more than 20 km for a decent catch. It is a livelihood loss for these fishermen.
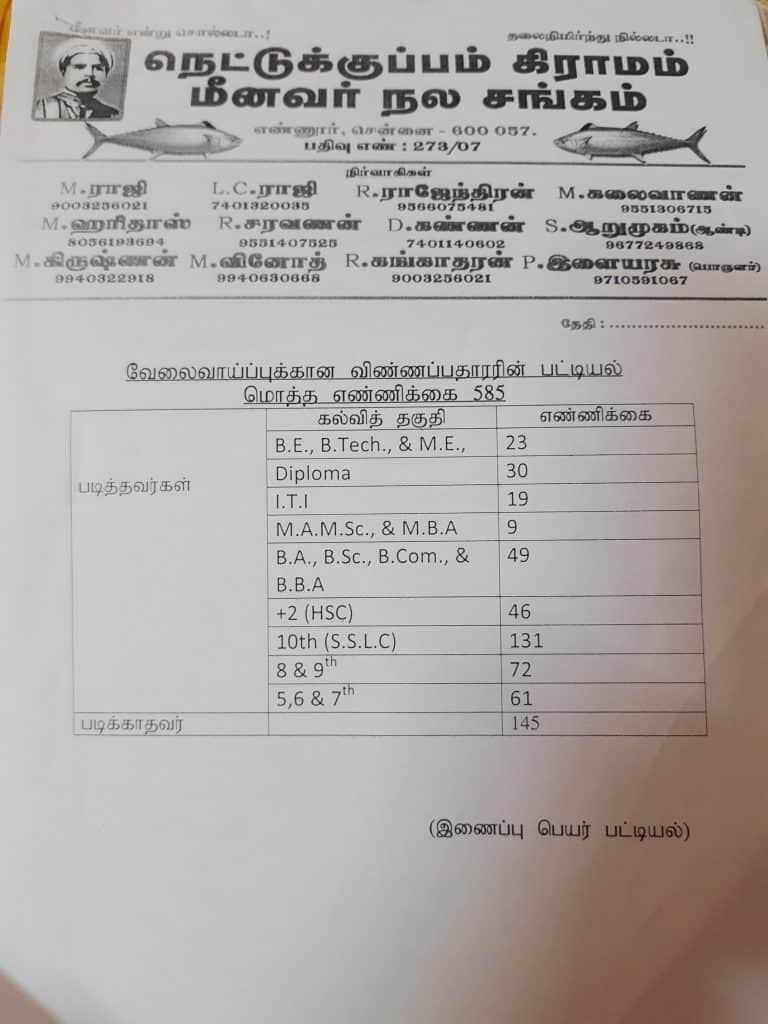
Ironically, the presence of more than 10 industries and nearby ports has not benefitted the locals. Unemployment is the norm, with around 585 youngsters searching for jobs at Nettukuppam village itself. The fishermen association at the village compiled the list.
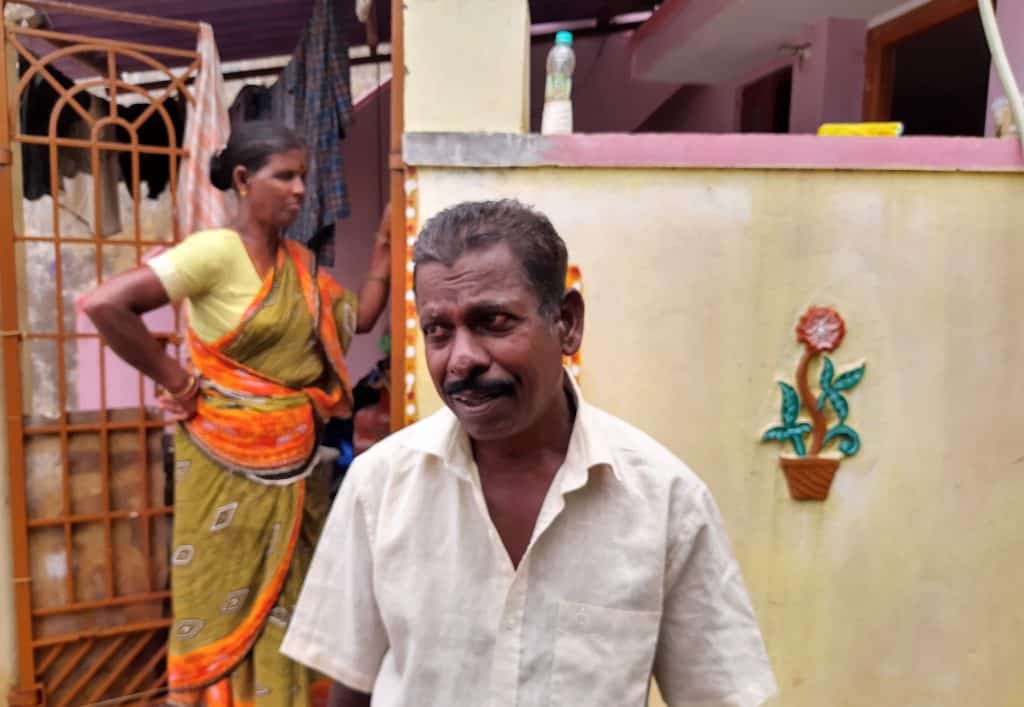 At least half of the fishermen have switched to other mundane jobs. A few old-timers such as L Panjanathan rely on fishing, even though it only means losses.
At least half of the fishermen have switched to other mundane jobs. A few old-timers such as L Panjanathan rely on fishing, even though it only means losses.
Fishing had economically empowered a lot of women twenty years ago. Cleaning and selling the fish in the markets used to be the women’s job. Now, with fishing hitting rock bottom, women are unemployed too. They are now willing to make a living by doing domestic chores or any decent work that fetches them some money.
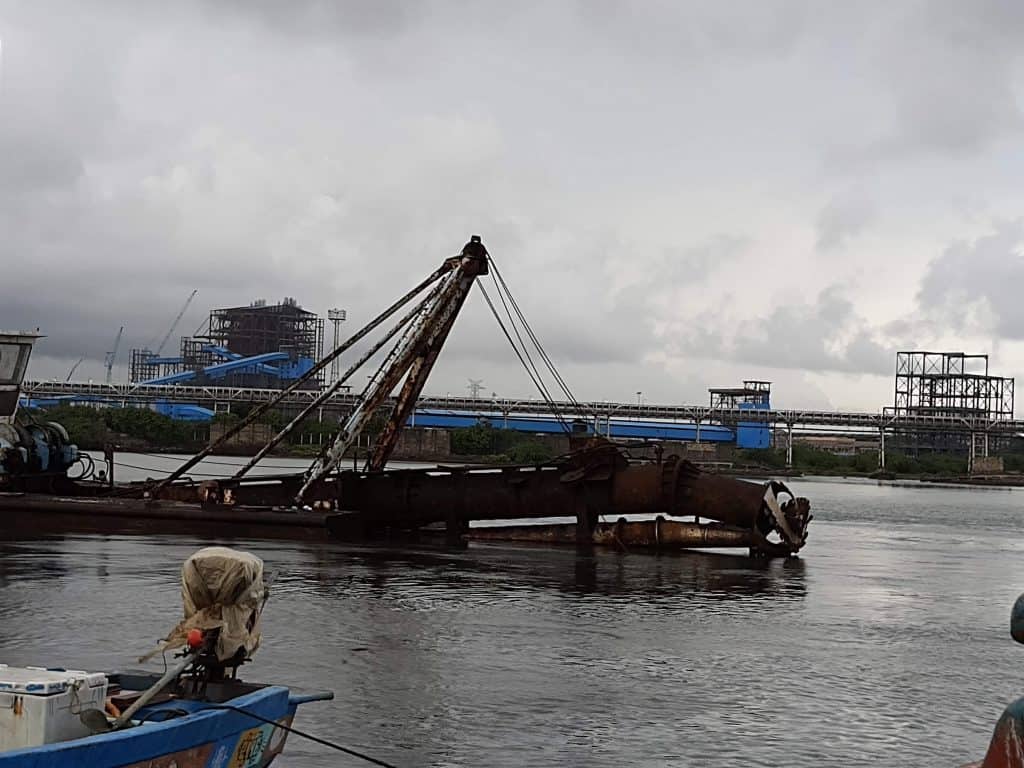 The National Green Tribunal has ordered the Ennore Thermal Power Station to dredge the river so that its mouth doesn’t get blocked (which will result in inundation during floods). The power station followed the instructions for a few months, but abandoned the exercise many months ago. The equipment lay idle when we visited the spot around 4.30 pm a week ago.
The National Green Tribunal has ordered the Ennore Thermal Power Station to dredge the river so that its mouth doesn’t get blocked (which will result in inundation during floods). The power station followed the instructions for a few months, but abandoned the exercise many months ago. The equipment lay idle when we visited the spot around 4.30 pm a week ago.
This is Kothari Fertilisers at Periyakuppam spewing toxic gases into the atmosphere. Next to the fertiliser company stands a row of houses, residents of which are the direct victims of this pollution. “It cannot be a coincidence that at least one person in the house has respiratory problems such as wheezing and asthma. My 12-year-old daughter has asthma,” said a resident, seeking anonymity.


Thank you for articles on Chennai… Very informative
Well written….highlights the plight of the marginal communities in encore….
Talk more about ennore pollution;