In the aftermath of the devastating floods of 2015 and the drought that hit Chennai, the focus on conservation of water bodies has been amplified. The many lakes of Chennai that have suffered years of neglect have begun to get a fresh lease of life with restoration efforts taking place across the city.
The Environmentalist Foundation of India is an NGO that has been playing an active role in the restoration of lakes along with other non-profits and civic agencies including the Greater Chennai Corproation and Chennai Smart Cities Limited.
While lake restorations of this scale are multi-year, ongoing activities, the progress seen in the lakes that have been restored to their natural states is a positive development that provides hope.
Here is a snapshot of the restoration process that has been followed by EFI in the Alleri Tank, Madambakkam Lake, Vandalur Lake and Kolladi Lake.
Alleri Tank Restoration
Located within the M.E.P.Z, the Alleri is an important water body located between the larger Kadaperi and Thiruneermalai lakes. A collaborative conservation effort between M.E.P.Z, DXC Technology and the Environmentalist Foundation of India (E.F.I).
Madambakkam Lake Restoration
Madambakkam lake in the southwest of Chennai is one of the largest lakes in the city and indeed a boon to be discovered for us at E.F.I. A collaborative effort between PWD, Government of Tamil Nadu, and the Rotary Club of Madras, south has facilitated E.F.I in reviving the lake of serenity.

The island with neem tree has been constructed to conserve the species and would be a natural nesting place for birds and other reptiles in the near future.

These are recharge pits for the water body that are used to increase the water holding capacity and recharge the groundwater level.

Vandalur Lake Restoration
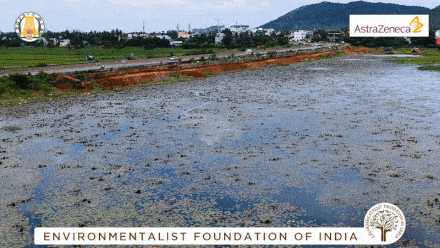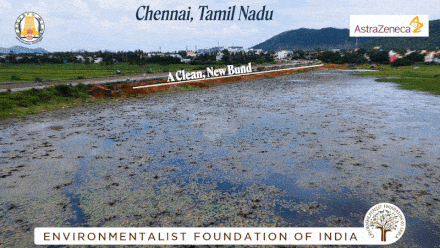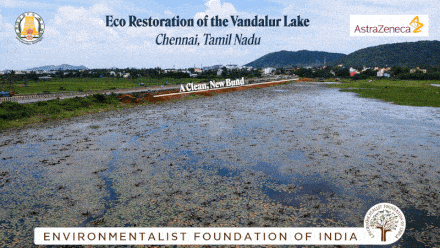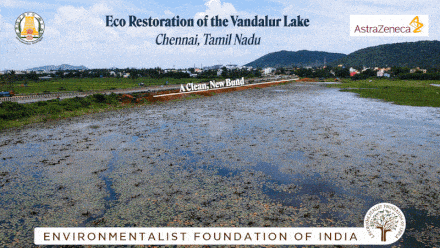
The Vandalur lake is situated in the southwestern part of the metropolitan city of Chennai. A collaborative effort between PWD and AstraZeneca has facilitated E.F.I in the refurbishment efforts of a disowned water body for the nature to bounce back with its at most resources.
Koladi Lake Restoration
The Koladi Lake restoration. An Eco-Paradise in the making. E.F.I with support from Thiruvallur District Administration and the Rotary Club of Madras has taken on the ambitious task of reviving this lake.
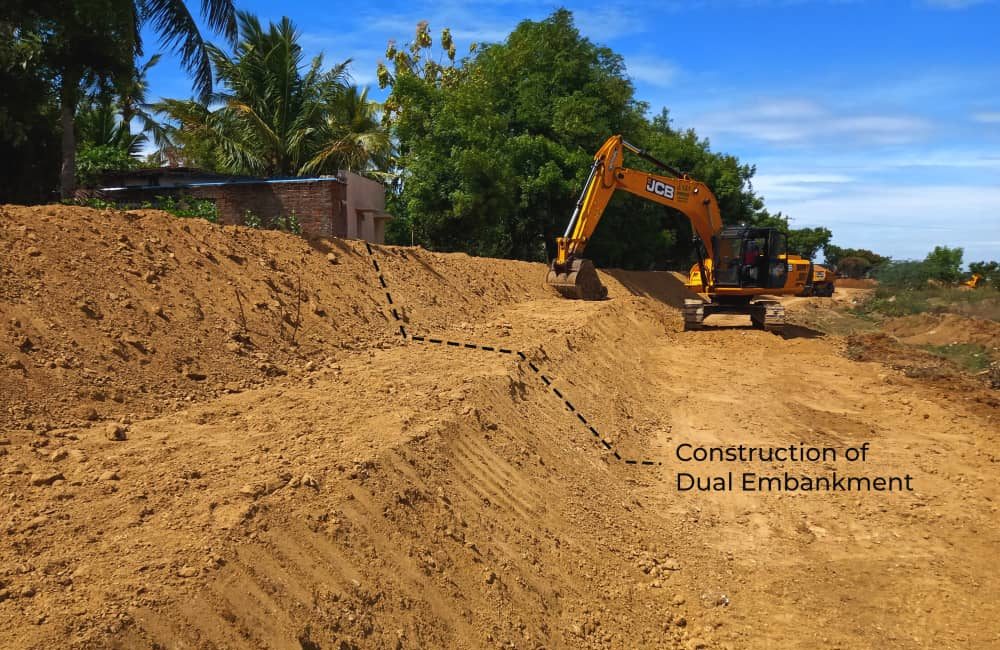
Construction of dual embankment prevents rapid soil erosion and protects the lake from further dumping of waste.
Also read:
We must ensure that environment conservation is as exciting as a TV Show: Arun Krishnamurthy, EFI
71 done, 139 in progress: Efforts to restore Chennai water bodies show promise
[This post was originally published in the blog of Environmentalist Foundation of India and has been republished with permission]