With nearly one-third of the world’s population under lockdown, once busy roads and streets are now empty, and public transit ridership as well as train and air travel have dropped significantly. The pandemic has slowed down the use of transportation systems and infrastructures.
Under these circumstances, transport infrastructure and services around the world are being modified for reduced demands and to meet COVID-related safety standards. But some cities are going as far as to find entirely new ways to continue using existing transportation infrastructure.
Adaptive reuse is the process of converting a building or structure to serve a function other than which it was originally built for. While the term is usually used for buildings, it is proving to be applicable to transportation services and infrastructure in response to the COVID-19 crisis.
Here are several examples from India and around the world of adaptive reuse of various modes of transportation:
Cycles as safe delivery systems
Cycling helps people commute while keeping a safe distance from others and hence, has become the safest way to deliver essentials to elderly neighbours and people in need. For example, a Bengaluru initiative called Relief Riders consists of volunteers on cycles supporting the elderly.
Doctor on wheels
The lockdown caused clinics and out-patient units at hospitals to close, hindering general health check-ups for those with non-COVID-19 or existing health conditions. To address this, a Bengaluru doctor converted his motorbike into an “ambulance” to visit patients in his neighbourhood to treat minor illnesses and provide them with medicines.
A new use for roads
With people working from home, journeys on foot and cycle have increased. In most places, existing sidewalks and cycle tracks are inadequate to maintain safe distance. As a response, several cities around the world from New York to Bogota have temporarily closed streets to vehicles to provide more space for people to walk and cycle.
Cars have alternative use too
Self-driving cars such as Toyota’s Pony.ai are delivering packages from e-commerce platforms in California. Additionally, the widespread car culture around the world has facilitated the setting up of drive-through testing centers. Delhi, Mumbai, Gurgaon (Gurugram) and Chandigarh are some of the Indian cities that have set up drive through centres.
Repurposed rideshare and taxis
Taxis and rideshare companies like Uber and NYC’s taxicabs are partnering with cities and supermarkets to deliver essential supplies.
Parking lots used differently
Many hospital parking lots have become drive-though testing sites and treatment facilities with beds as in Nashville’s Vanderbilt University Medical Center. Parking lots of movie theatres, restaurants, and other businesses are being converted to drive-in movie theaters as in Mingus, Texas.
Buses as WiFi hotspots
The lockdown caused schools to close and not all students have access to the internet. To address this roadblock to distant learning, cities such as Austin, Texas, equipped their buses with WiFi and stationed them in areas where students require these services.
Buses repurposed for emergencies and more
Buses in Toronto have been repurposed to support the growing demand for ambulances to transport stretcher-bound patients. They have been equipped with medical devices including ventilators. Similarly, in Karnataka, KSRTC buses are now being used as ‘mobile health check-up clinics’. In several other places worldwide, buses are proving to be an efficient option to deliver food to people in need.

Supermarket on wheels
Across Canada, Grocery Neighbour is equipping a fleet of trucks to enable them to operate like a supermarket on wheels and provide residents the option to shop for a range of products from the safety of their homes.
Trains reused in multiple ways
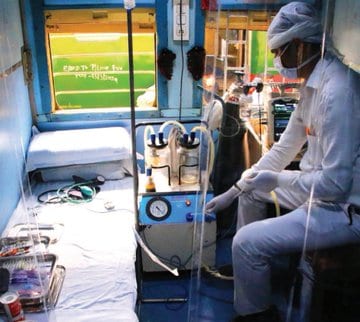
India’s railway network shut down for the first time in 167 years. They engaged the workforce to convert as many as 20,000 old train carriages into isolation wards for patients. Similarly, France converted trains into mobile care units for critical patients.
Boats as isolation wards
Due to a drop in tourism and trade, boats are now empty. Boats and ships around the world are being converted into isolation wards including houseboats in Kerala.
Shipping containers to field hospitals
Shipping containers have been converted to intensive care pods with the first fully operational unit in an old train repair facility in Turin, Italy to provide additional facilities to treat patients and relieve overcrowded hospitals.
Airports as drive-in cinemas
Lithuania’s international airport in Vilnius, converted its airfield to a drive-in cinema. With both airports and cinemas stalled at the moment, this initiative creates a unique “Aerocinema” drive-in experience.
Airports as hospitals
While still a proposal, architects are suggesting that cities transform airports into hospitals. They claim these solutions can be implemented in any airport in the world while airport traffic is witnessing a downtime.
As seen in the examples above, this pandemic has spurred a wave of creativity around the world. This situation serves as a learning opportunity for us to re-examine our urban environments and help us act responsibly to inform the future of our cities.
These innovative ideas can either remain temporary and be forgotten, or be connected to permanent and positive change. For example, 20 miles of temporary closed streets in Seattle will be permanently closed to through traffic. This decision aims at encouraging a walking and cycling culture in the city.
We cannot let these lessons be wasted. It is not only during emergencies that we need to think creatively about what to do with empty buses or old train coaches, we can actually do this all the time. While some cities have applied adaptive reuse concepts before, such as London and Athens, Georgia, more cities need to follow suit and embrace these sustainable practices.
Adaptive reuse solutions need efficient, effective and flexible plans. A system that is agile and serves varying needs is truly resilient and sustainable.
In the future, whether it’s another pandemic or crisis of a different nature, these learnings can help prepare our transportation systems to adapt quickly while fulfilling their original purpose of moving people and goods safely.
Very informative article. Compiled and written well. I totally agree with you on the point that people should learn from this pandemic and make permanent adaptive changes for a better future.
This excellent article offers a new perspective on how we can use and reuse the available infrastructure around us, but also on how we should anticipate during the conception phase the ever growing need of more versatile and adaptive usage options.