Karnataka presently generates around 500 tonnes of biomedical waste per month. Over 70% of this ends up in landfills, contaminating soil, water and air. Part of this includes medicines, which has only increased with the COVID-19 pandemic. While hospitals and clinics account for the bulk generation of the waste, they are governed by the Hazardous and Biomedical Waste Management Rules 2016, set out for them. This ensures that many of them follow some basic guidelines on responsible disposal of bio-medical waste.
However, at the household level, there appear to be glaring gaps in the manner in which medical waste generated is managed. And much of it can be traced to the lack of compliance with the segregation guidelines in waste management rules.
Segregation: Mandates vs practice
Under the Solid Waste Management Rules 2016, household waste needs to be segregated into three categories :
- Biodegradable/Wet Waste – kitchen, garden and horticulture waste
- Non-biodegradable/Dry Waste – plastic, cartons, disposable waste and E-waste
- Domestic Hazardous Waste; Sanitary Waste
Sanitary waste includes menstrual waste (used panty liners, sanitary pads and tampons) as well as used condoms, syringes, diapers, medicines, cotton and bandages, all of which contain bodily fluids and are categorised as domestic hazardous waste.
Medicines are not specifically mentioned, but are often disposed of as part of dry waste and this is where a large part of the problem lies.
Households generate all kinds of medicinal waste, including syrups, vitamins, protein supplements, capsules, antibiotics, veterinary meds, allopathic, homoeopathic and ayurvedic, etc. In addition, there are sanitary wastes such as menstrual pads, diapers, syringes, cotton swabs, etc., all of which need to be segregated from dry and wet, packaged in newspapers and kept in red dustbins for clear identification and proper disposal by the agency.
Unused and expired drugs need to be disposed NOT in the dry waste collection stream, but in the sanitary waste stream of waste.
Read more: All you need to know about donating unused medicines in Mumbai
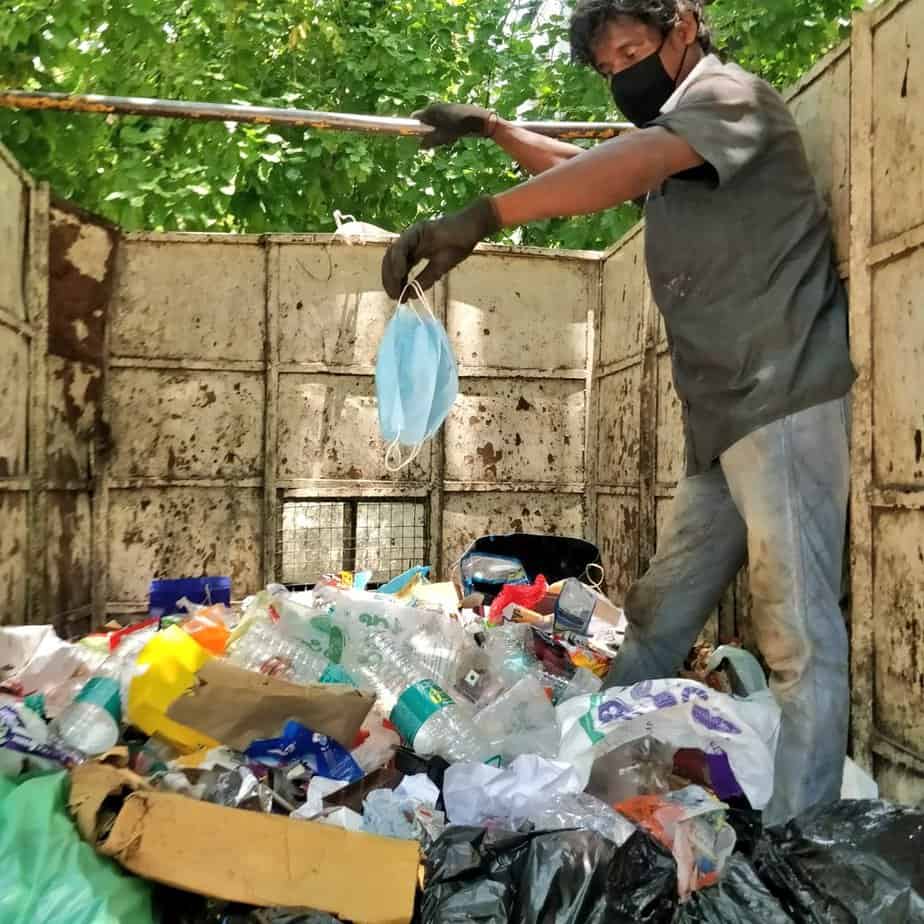
In reality, however, we find that segregation levels are very poor in most cities including Bengaluru, and we have seen medicinal waste being disposed of with dry waste, or worse, being flushed down the toilet.
This causes our landfills and water bodies to be heavily contaminated. Studies have also shown that this causes bioaccumulation in humans and animals leading to antibiotic resistance. In addition, India’s rag-picker communities have the horrible task of sorting (segregating recyclable material from the heaps of historic waste piled up everywhere) our waste in the most inhuman of conditions. Medicinal waste is the most dangerous for them to handle.
What about bulk generators?
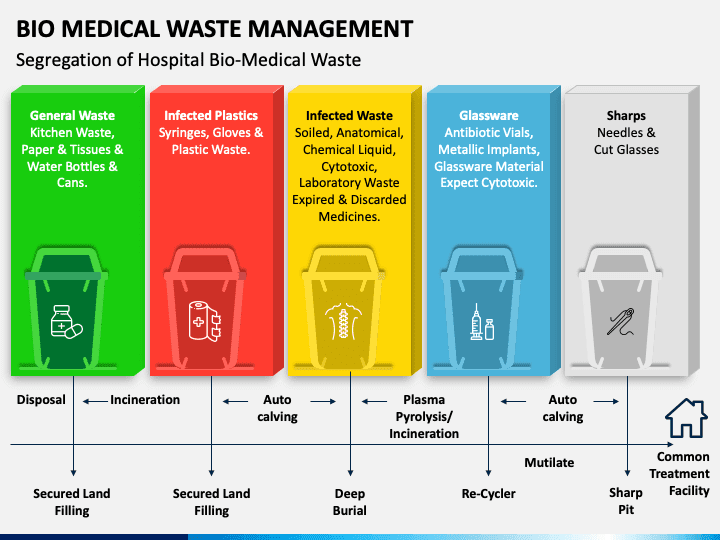
Today hospitals and clinics manage their own waste — the segregation and disposal of the same, which is comprised of:
- Items contaminated with body fluids: Dressings, plaster casts, cotton swabs and bags containing residual or discarded blood and blood components.
- Expired or discarded medicines: Pharmaceutical waste like antibiotics, cytotoxic drugs including all items contaminated with cytotoxic drugs along with glass or plastic ampoules, vials etc.
- Discarded linen, mattresses, beddings contaminated with blood or body fluid.
- Tubes, bottles, intravenous tubes and sets, catheters, urine bags, needles, scalpels, blades, syringes (without needles and fixed needle syringes and vacutainers with their needles cut) and gloves.
In Karnataka, 82604 kg/day of biomedical waste is generated largely by the clinics and hospitals. While some of the large generators have in-situ or captive treatment facilities, there are about 25 common biomedical waste treatment facilities (CBWTF) in the State, where a total of 37805 kgs/day is treated.

Ways to reduce biomedical waste
Medications are sold in standard sizes; for example, tablets/capsules are sold in strips of 5/10 etc., often leading to wastage. There are a few options available to dispose of or donate your unused medicines if they are still usable.
- If there are strips of unused medicines that are not expired, one is encouraged to hand it over to the local pharmacy for further use.
- There are a few NGOs such as MedsForMore that accept these.
- Only a few Primary Health Care Centres (PHCs) accept unexpired medications. It can be handed over to the medical Officer. [The complete list of PHCs can be found here.]
- If the quantities are huge it can be handed over at the BBMP head office.
- Some hospitals like St John’s have a drop box for the medicines which have not expired.
Attach the list of unused medications, along with the quantities and expiry date. Please evaluate exactly what they do with these medicines and how they re-purpose it before you donate, so that they are not misused or they do not end up in the wrong hands.
Read more: How to dispose of pet waste
Ways to dispose of biomedical waste
We can reduce a part of this impact through segregated and responsible management of unused and expired medicines. Environmental Synergies in Development (ENSYDE) has spearheaded a one-of-a-kind initiative to ensure responsible collection and management of medicinal waste generated at the household level. This initiative, Be the Prescription for Change, aims to provide citizens with a responsible solution for the collection and management of their unused and expired medicines.
ENSYDE provides Resident Welfare Associations (RWAs) with awareness, collection boxes, and tie-ups with Karnataka State Pollution Control Board-authorised disposal and treatment agencies.
Key challenges to this initiative include:
- Lack of awareness on the importance of this issue;
- Reluctance of RWAs to pay for the management of another stream of waste;
- The expenses of collection from dispersed locations and logistical problems faced by the authorised collection/disposal companies because of low volumes.
Currently, ENSYDE has placed 25 collection boxes in apartments (see box), and is in discussions to place 50 more in RWAs/pharmacies within the next few months. We hope to increase the participation and ensure that all citizens in the city have access to this facility. Once the collection boxes are full, the RWA calls Maridi Bio Solution Pvt. Ltd., with whom they have signed an agreement for future collection, transport and disposal.